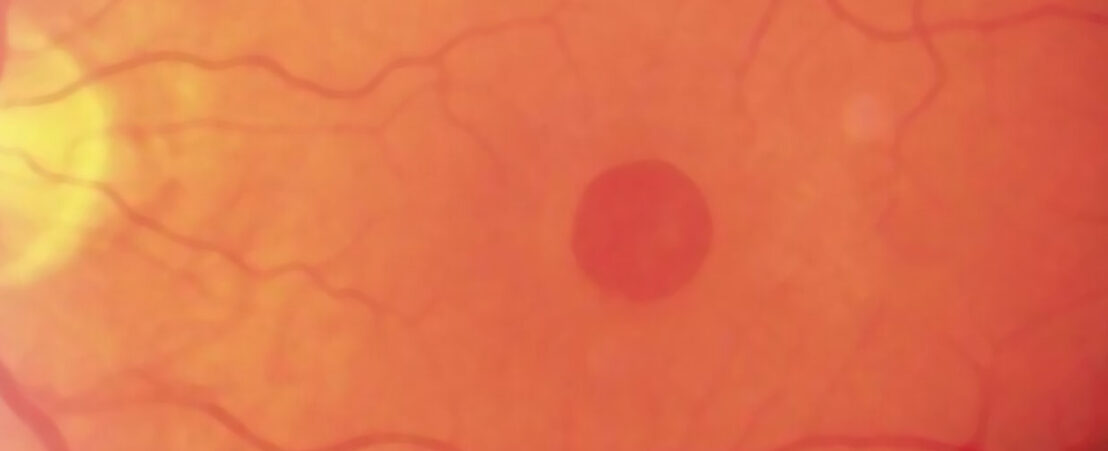
A macular hole causes loss of central vision and image distortion in the eye. The distortion is manifested as a bending or waviness of straight lines or objects can begin to look bent or wavy and numbers and letters jump out of line.
Other symptoms manifested by patients are a central grey spot or a blind spot in the central vision and difficulty reading.
The macular hole usually manifests itself in an acute way overnight, but sometimes the visual loss is more gradual and takes place during weeks or months. Sometimes patients don’t realize it until they come to cover the eye that is not affected.
In the early stages of the disease, a yellow injury in the fovea is detected. The fovea is the part of the retina located in the centre of the macula and is responsible for the detailed vision, necessary for reading.
When the hole is consolidated, it is displayed in the fovea.
IDIOPATHIC
It appears in healthy patients without evidence of other eye diseases. It is the most common type of macular hole and is related to advanced age.
SECONDARY
Determine whether any of the above-mentioned causes is responsible for the macular hole. If that’s the case, both problems would need to be treated.
Before solving the macular hole, we need to assess the degree of cataract of the patient. In patients who also suffer from a cataract, a combined surgery consisting in cataract extraction and macular hole surgery is recommended. This is performed in an only procedure in order to avoid the need to perform a second intervention later in time.
Macular hole surgery is performed in order to:
Cataract extraction is performed in order to:
The cataract extraction allows us to correct any refractive errors that the patient may have.
Patients with stage 2, 3 and 4 macular holes generally require surgery.
Patients with early stage macular holes (stage 1) that do not require surgery should be examined from time to time to assess whether there has been a disease progression and they will have to perform a self-monitoring at home with Amsler grid in order to determine whether there are changes in the distortion.
Patients should go to see the ophthalmologist before the scheduled date if there is a symptomatic decrease in vision or an increase in distortion.
Each examination will consist in the assessment of any vision loss or increase in image distortion. A macular OCT will be performed in order to assess whether there has been a progression in the macular hole stage.
Contact us or request an appointment with one of our specialists.