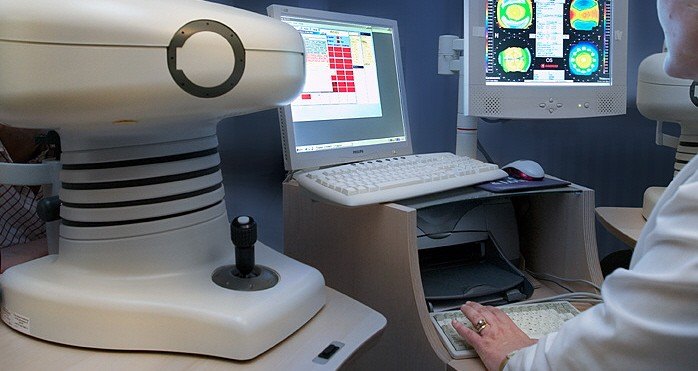
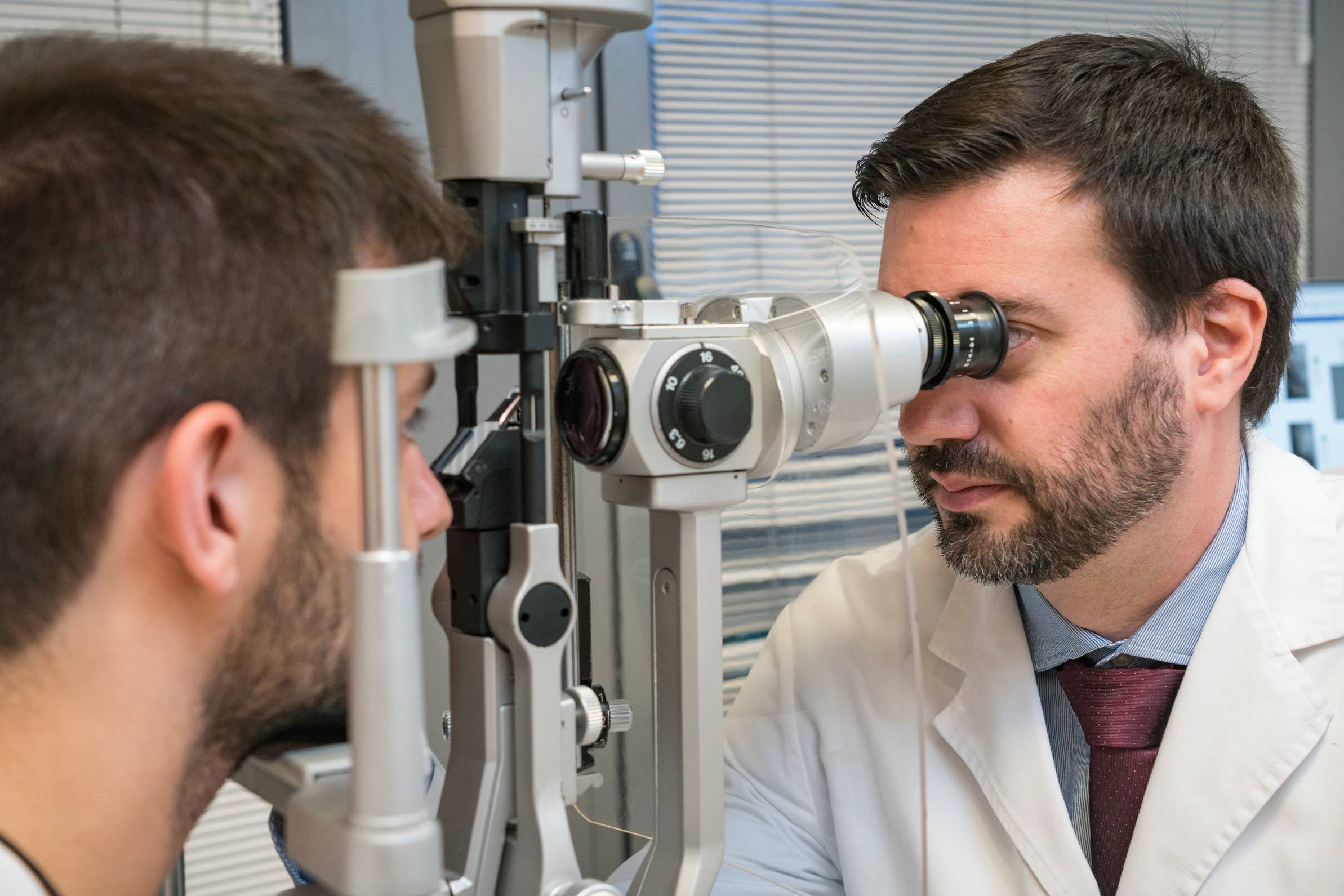
Aberrometry is a non-invasive ophthalmological test that allows studying the optical quality of the visual system. It does not contact the eye nor cause any kind of discomfort.
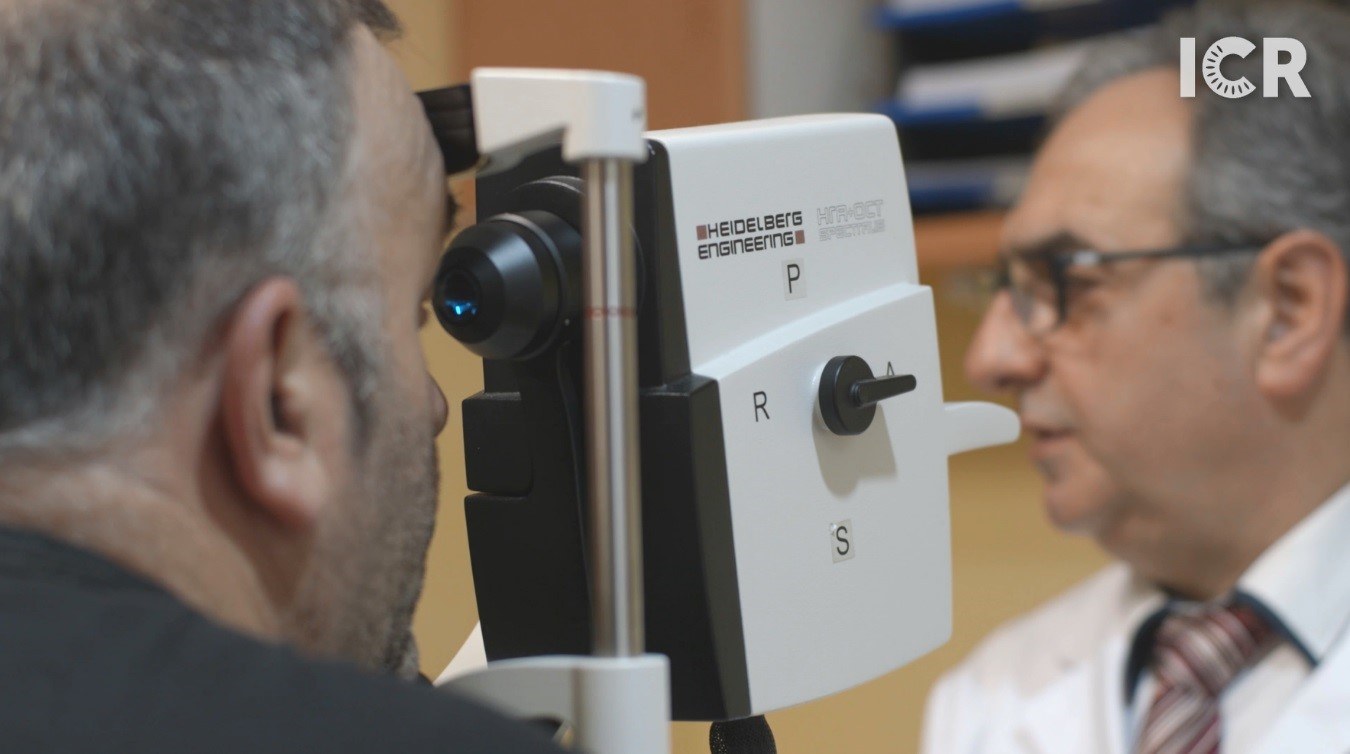
Fluorescein angiography is a test that
is performed by injecting a dye into the patient’s vein. This allows specialists to study the blood flow through the eye to diagnose different retinal illnesses.

Astigmatic queratotomy allows treating high astigmatism, either congenital or secondary to trauma, corneal deformations or post-operative.

CO2 Laser is a laser technology used in aesthetic treatments to improve the look of the skin or reduce injuries, with a shorter period of recovery.

Our goal is to ensure that our patients recover their vision and that they do so depending as little as possible on their glasses.
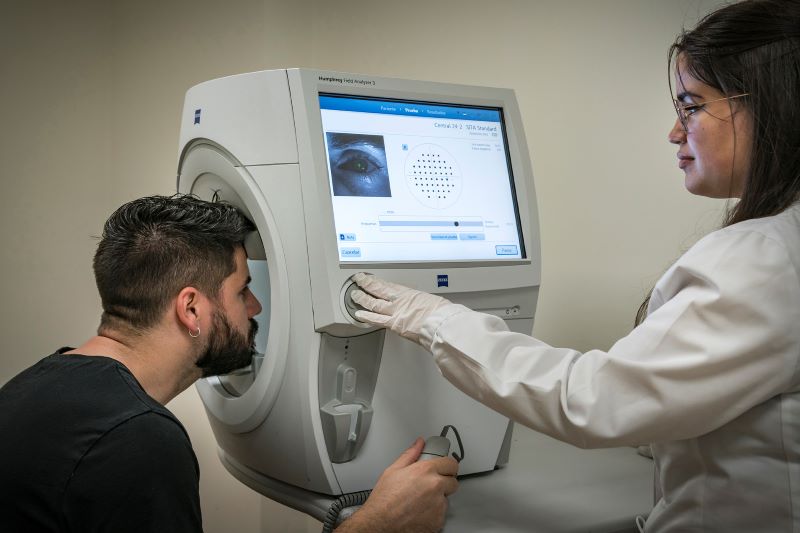
Measurement of visual field defects caused by diseases such as glaucoma or diseases that affect the retina or the visual pathway up to the cortex.
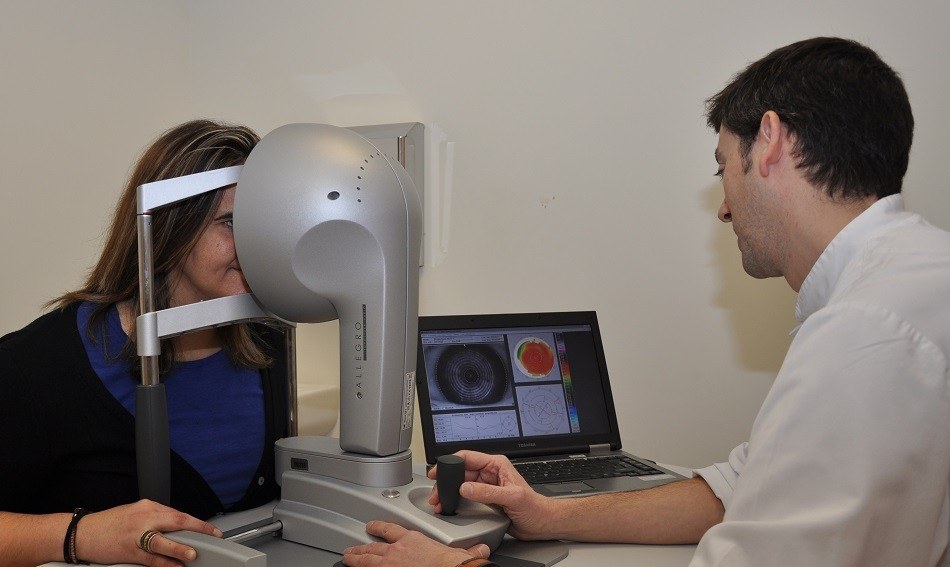
Study of the corneal morphology for refractive surgery, contact lens adjustment and the diagnosis and follow-up of diseases such as keratoconus.

Corneal transplant or keratoplasty involves replacing the opaque corneal tissue when a corneal scar causes visual loss. Keratoplasty is currently highly developed.
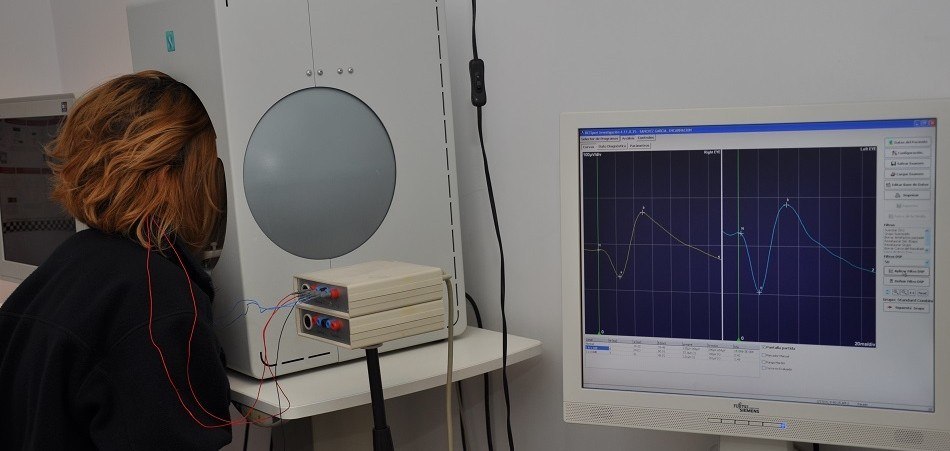
The electrooculography is an electrophysiological test used to evaluate the functional status of the retinal pigment epithelium, the alteration of which is related to some retinal diseases.
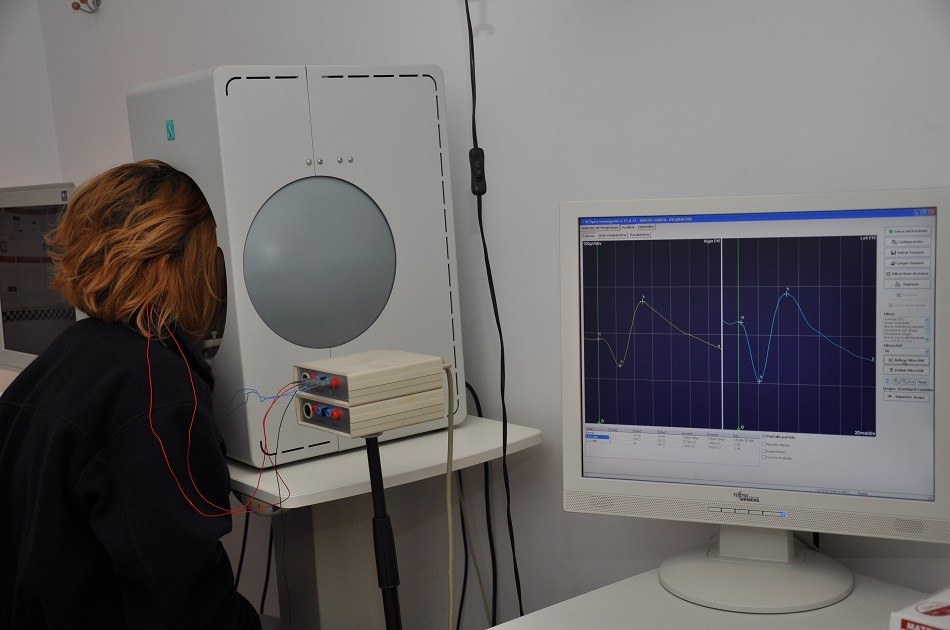
The electroretinogram is an electrophysiological test used to measure the electrical response produced by light-sensitive retinal cells. It allows the early detection of retinal diseases.
Intravenous injection of dye (sodium fluorescein or indocyanine), in order to study the diseases of retina and choroid. This test is performed in hospital.
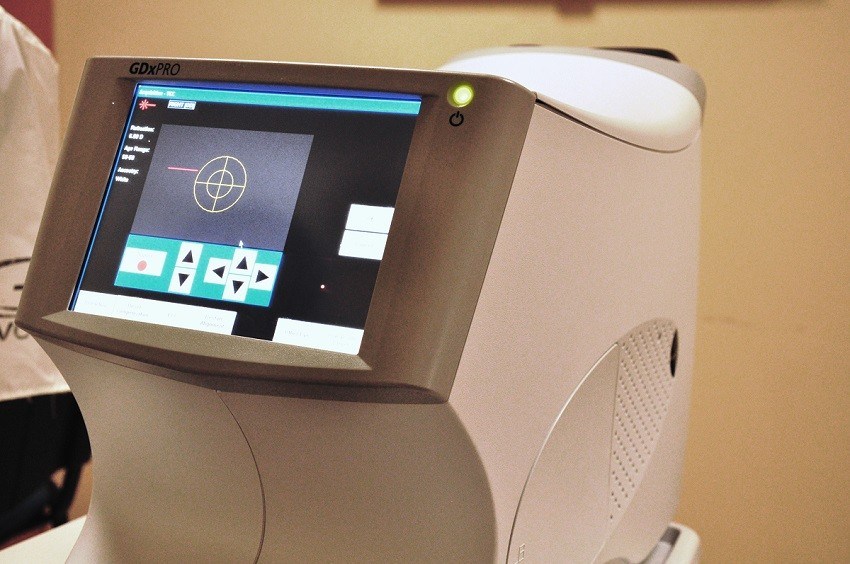
Laser analyser which assesses the nerve fiber layer injured by glaucoma. GDX improves early diagnosis.
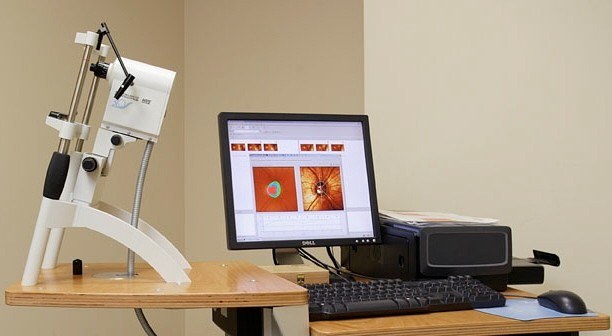
Confocal tridimensional laser scan of the optic nerve for the study of glaucoma. It provides a high resolution image of the elevation of optic disc and the peripapilar retina.
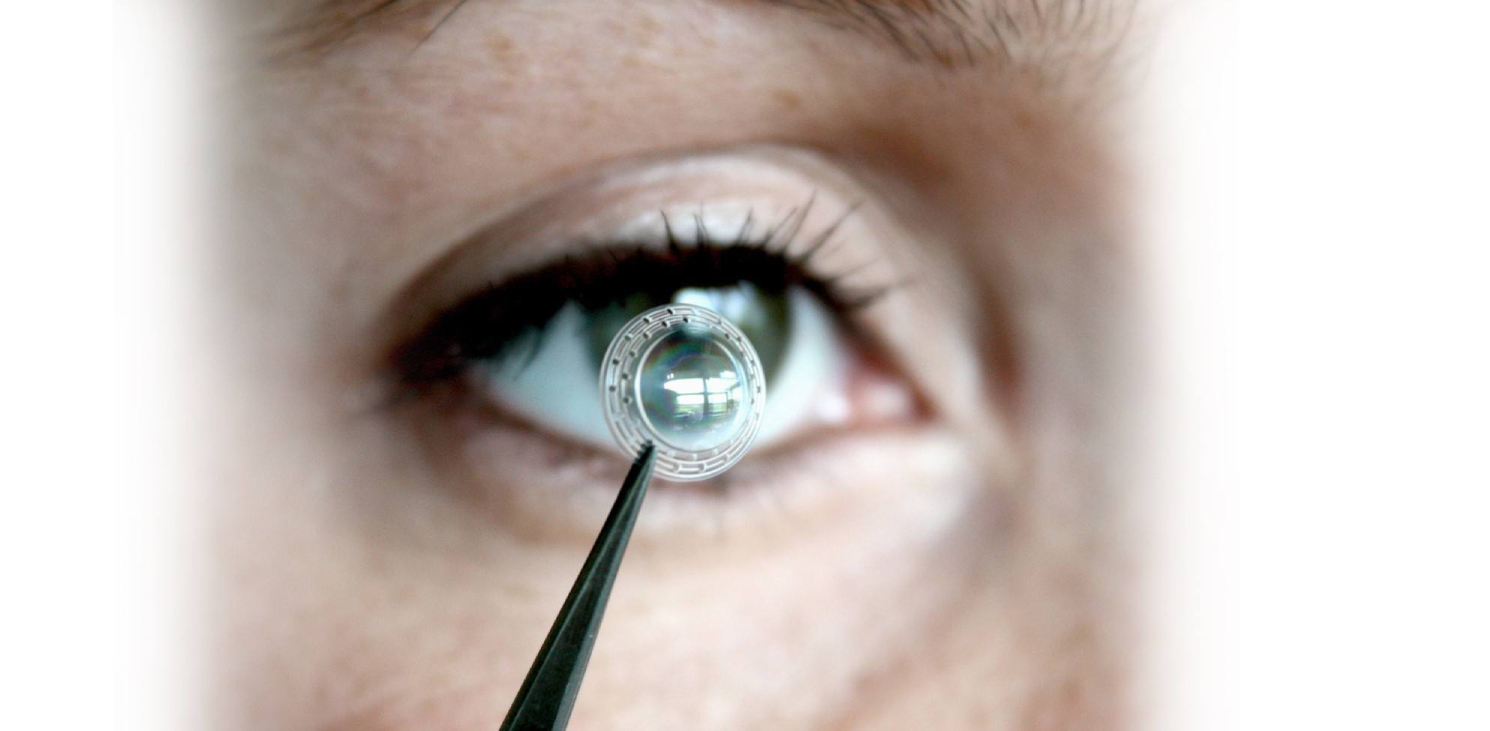
This surgical technique consists of introducing an acrylic plastic implant with the form of a ring in the corneal thickness, in order to reinforce the structure of the cornea.

Intravitreal injections are used to administer drugs directly into the vitreous cavity in order to treat eye conditions and protect vision.

The new laser systems serve to correct diopters and optical aberrations. These techniques include LASIK, LASEK, PRK, PTK and EPILASIK. The ophthalmologist will recommend the most suitable option for each patient.
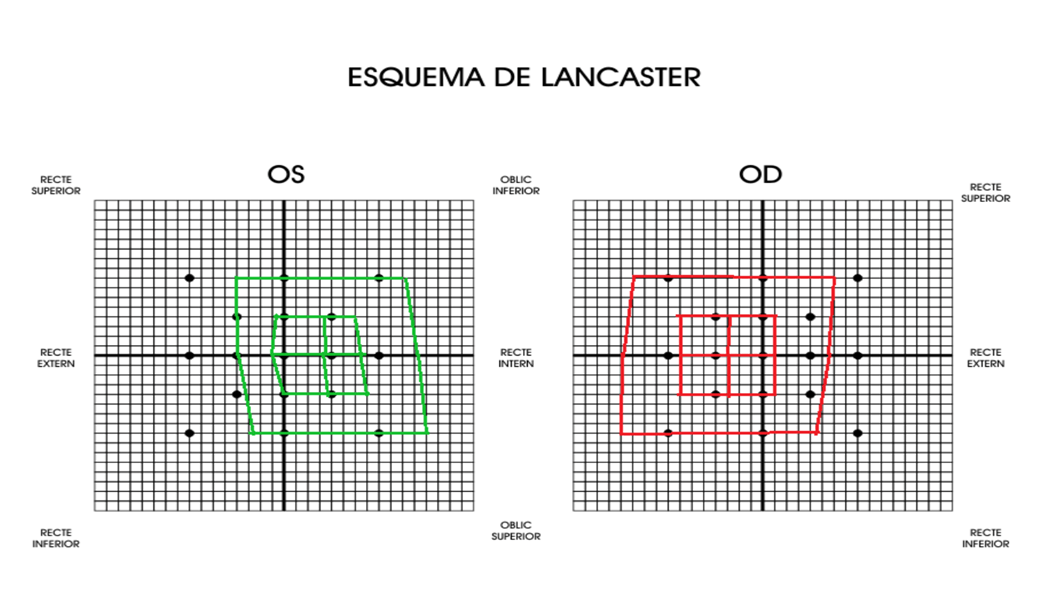
Non-invasive test used to evaluate the ocular motility to study some strabismus cases. It allows the identification of the eye muscles that present some alteration of mobility.
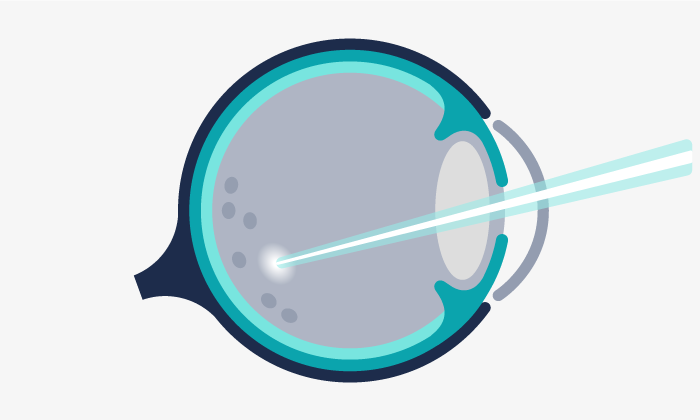
Photocoagulation is a therapeutic technique used in ophthalmology in which a scar is purposely made on the retina using a laser beam. This scar can slow down the progress of certain retinal diseases.
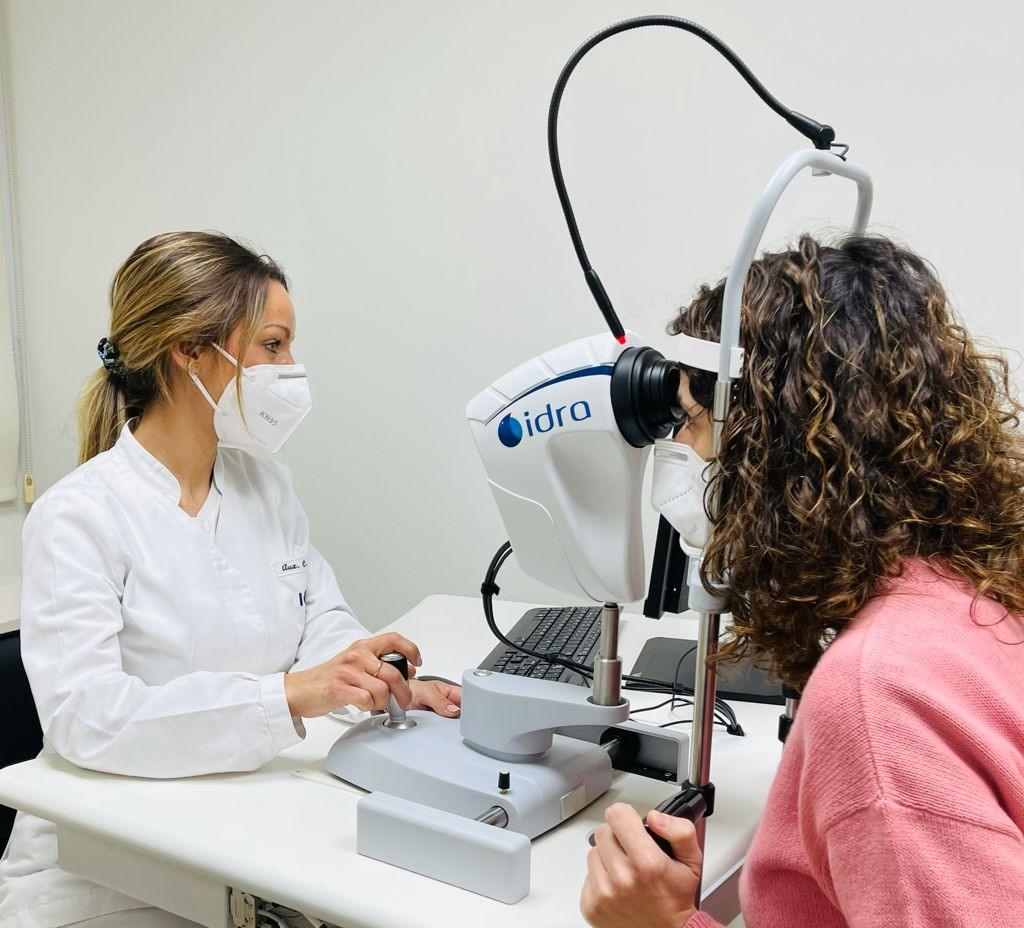

It is a test used for the detection and monitoring of possible dysfunctions of the meibomian glands and determine whether they fulfill their function of providing the necessary fats to limit tear evaporation.
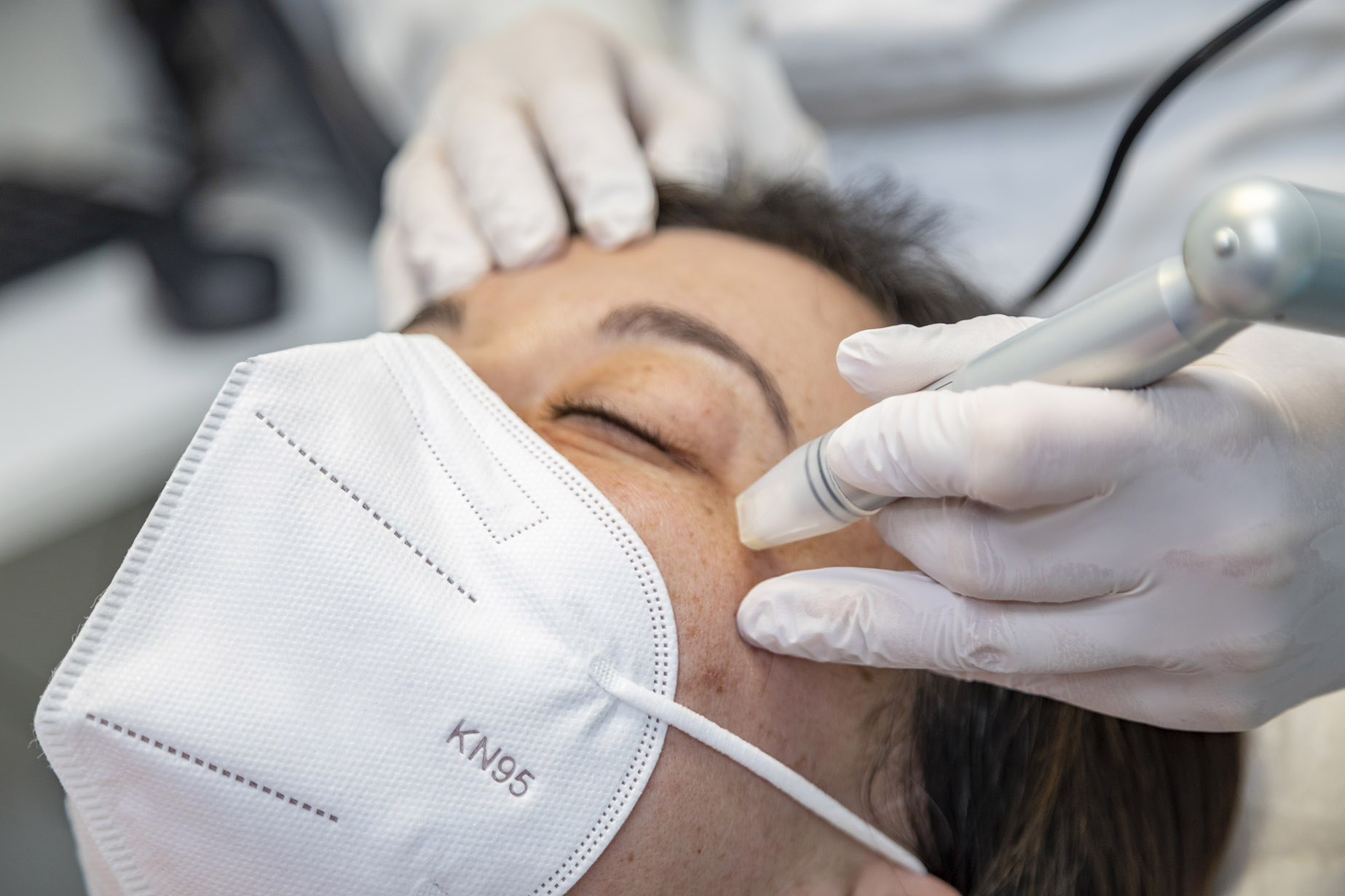
Cosmetic treatment that stimulates collagen production and can be used to introduce active agents, such as growth factors and hyaluronic acid to improve the look and quality of the skin.
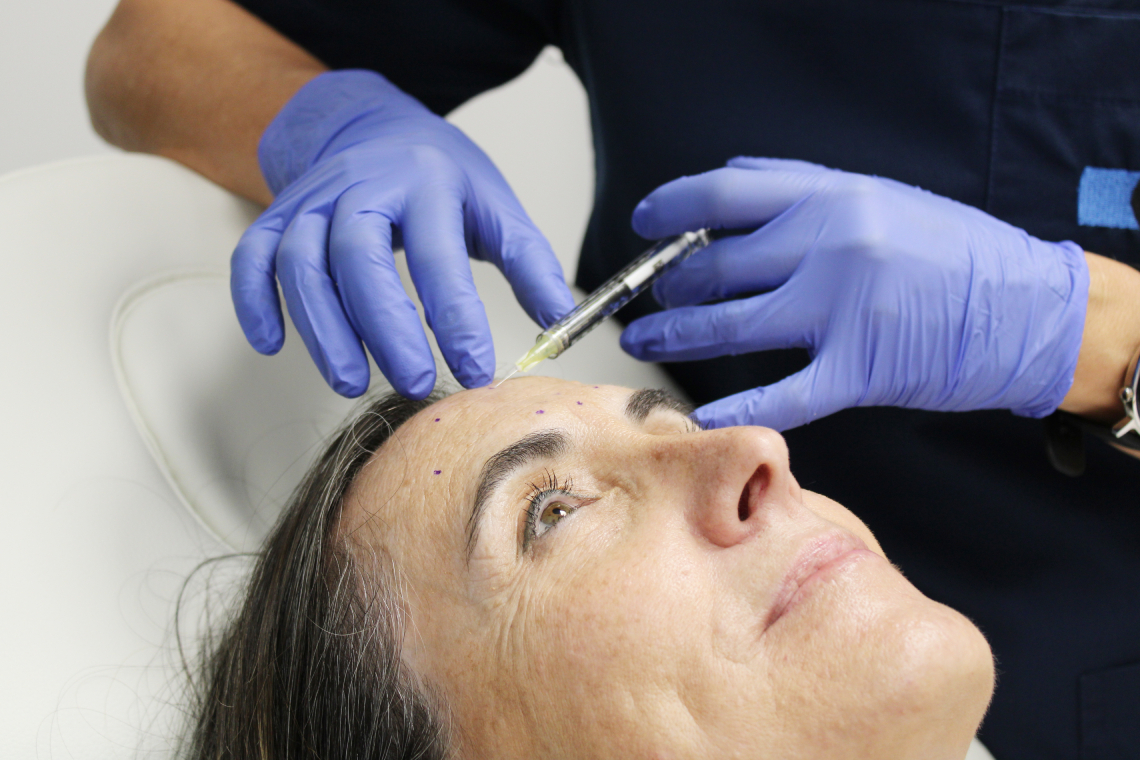
Neuromodulators (comercially known as botox) are used to treat medical conditions and to reduce aging signs, such as facial wrinkles.
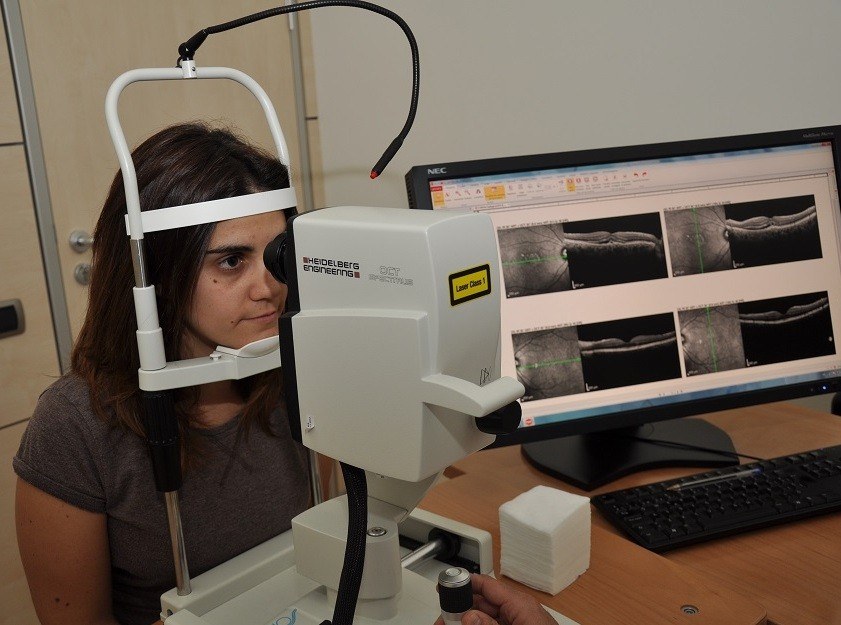
System used to obtain high resolution scan images of the tissues through laser. It is specially useful to study macular diseases and the optic disc.
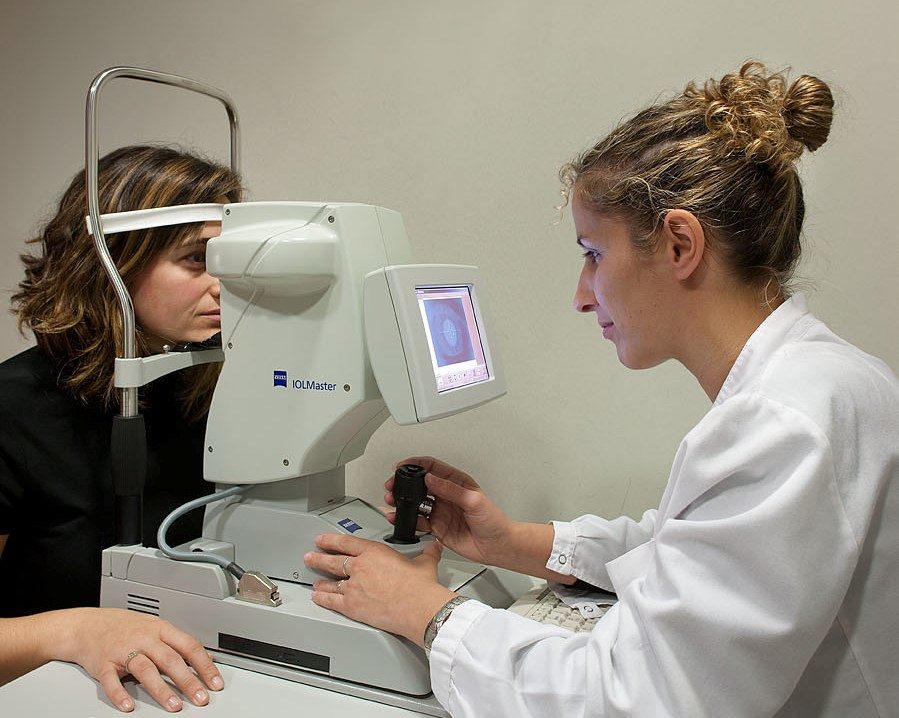
An ocular biometry is a test that measures the length of the eye to calculate the dioptric power of intraocular implants.
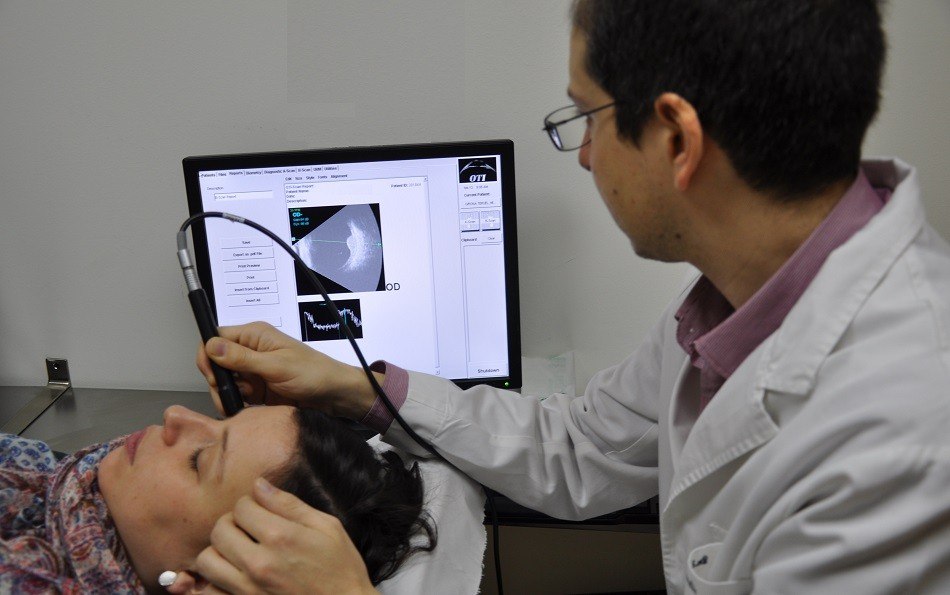
An ocular and orbital ultrasound is an imaging test used to obtain measurements and produce detailed images of the eye and its orbit. There are several types of ocular ecographies that serve different purposes.
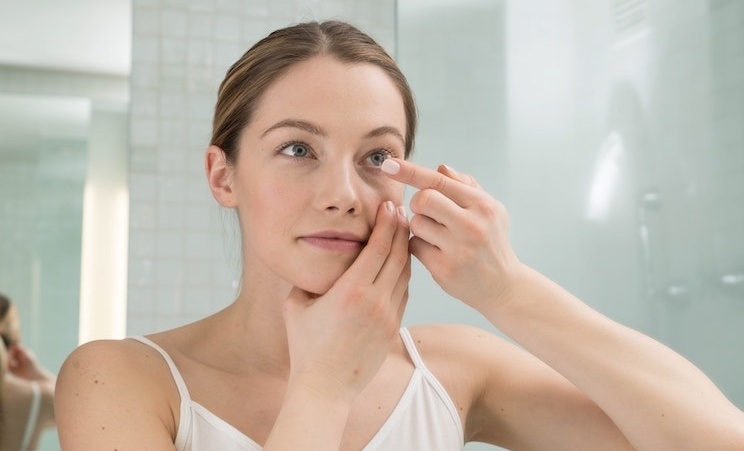

Orthokeratology consists of the adaptation of a specialised contact lens that exerts a shaping effect on the cornea at night, while we sleep. This allows the patient to see well throughout the day.
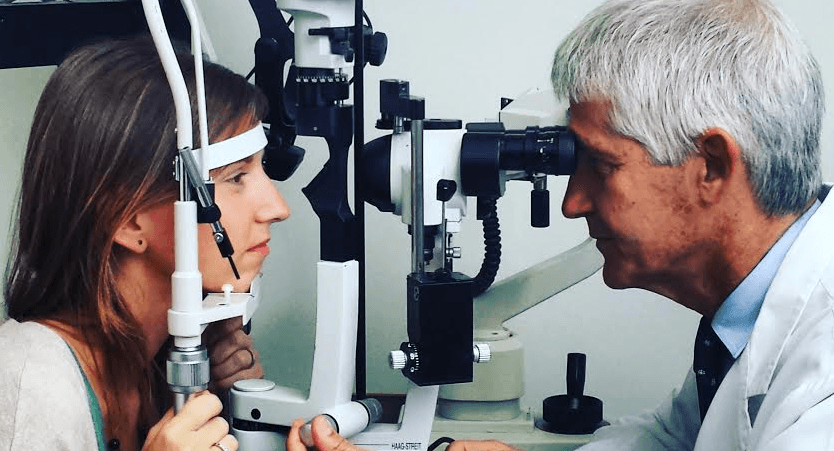
Recently, we have started to use state-of-the-art intraocular lenses which besides myopia, hyperopia and presbyopia, can also correct astigmatism efficiently.
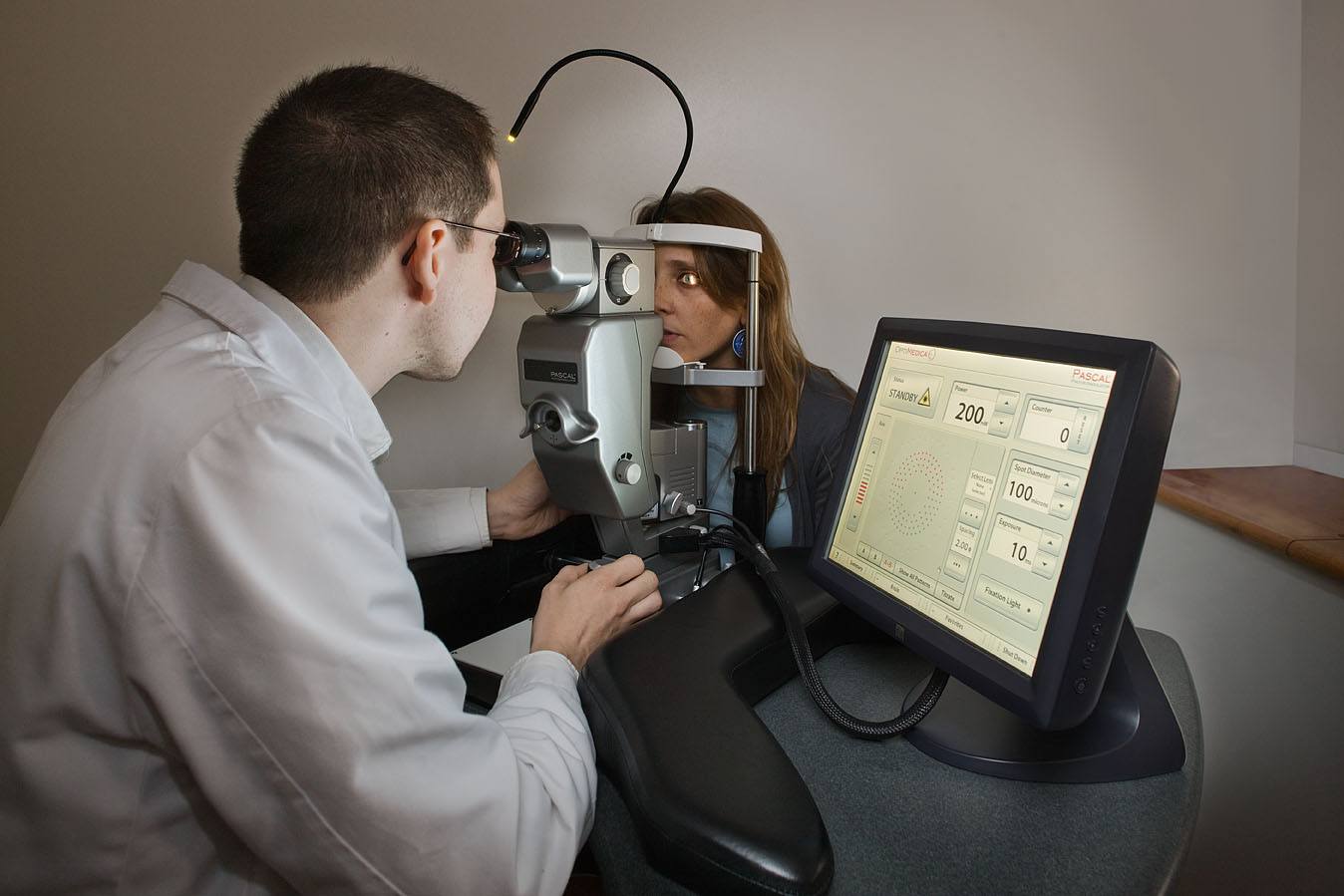
Laser treatment performed on the retina in cases of retinal tears and degenerations, diabetes and vascular occlusions. Also used for the treatment of open angle glaucoma.

Treatment of subretinal neovascularization in age-related macular degeneration. Patients are asked to protect their skin and eyes for 24 hours.

Presbyopia surgery is intended to correct the changes experienced in vision caused by presbyopia. There are several techniques available with laser and lens implantation.

Radiotherapy uses high energy rays to eliminate tumor cells of a specifically defined area. Directing radiation towards the eye helps to weaken the tumor.
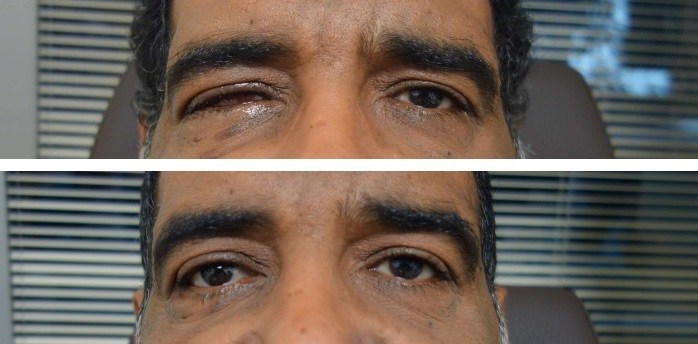
Some conditions require the reconstruction of the eye socket. It can be done through different techniques, including evisceration, enucleation and pericraneal grafts.
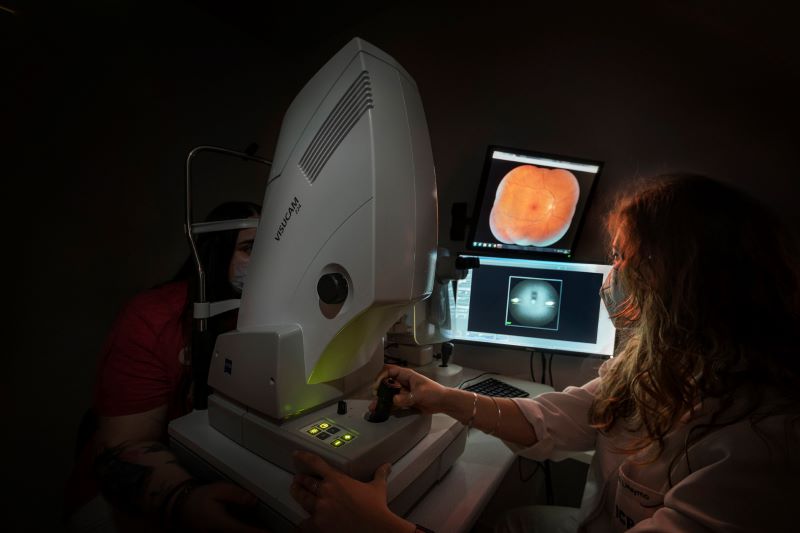
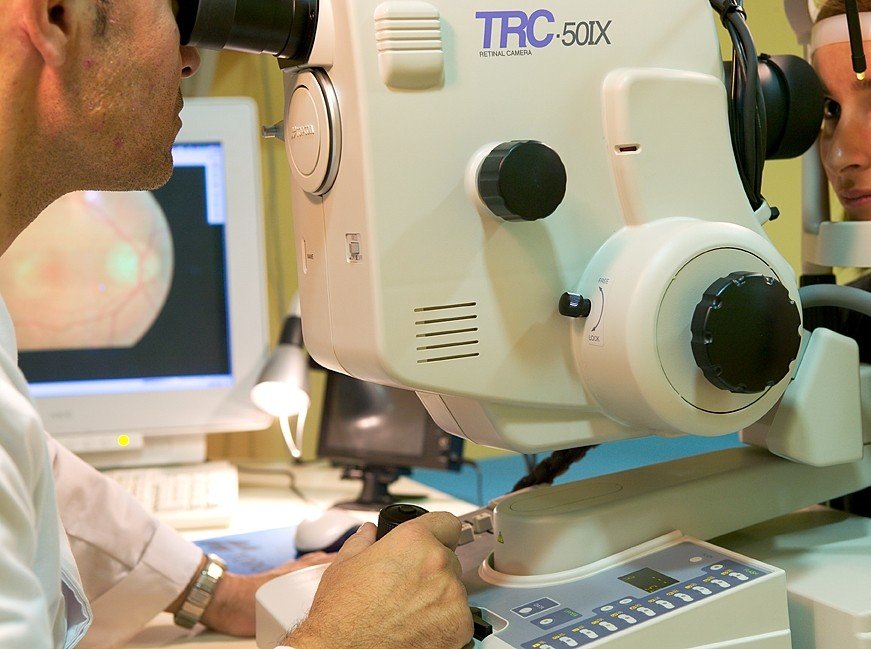
A retinography consists of taking coloured photographic images to control the progression of abnormalities in the fundus of the eye. It is used to detect retinal pathologies and to monitor glaucoma.
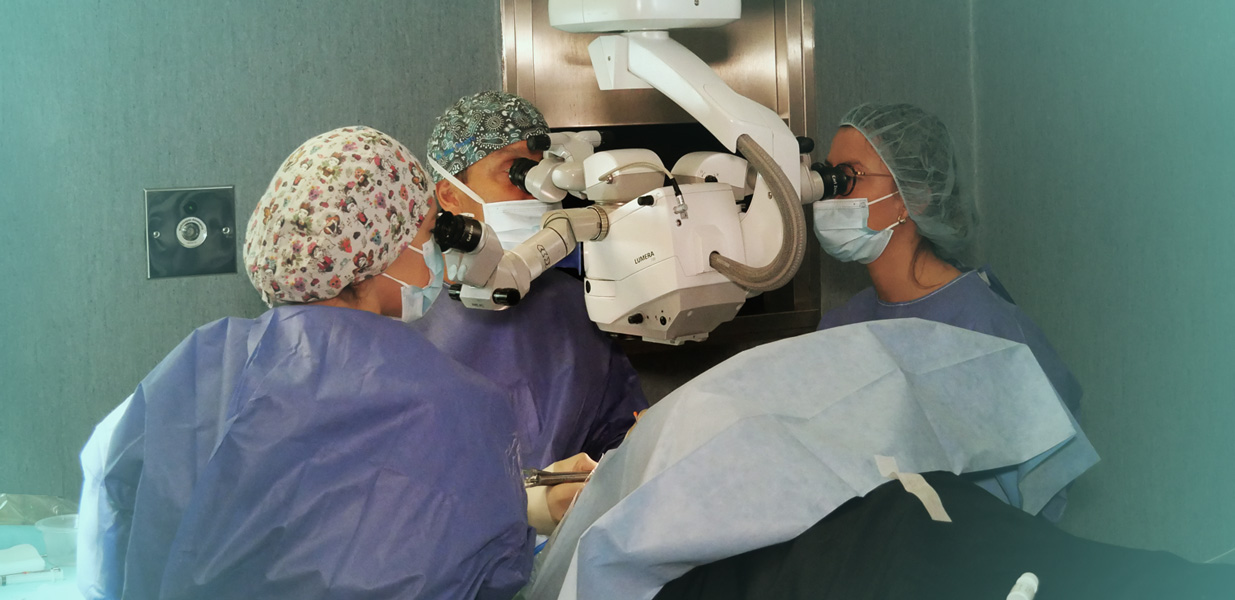
Simple scleral surgery is the procedure in which a ring made of silicone is placed in the sclera. It is useful for treating retinal tears, holes or breaks that have caused a detachment.
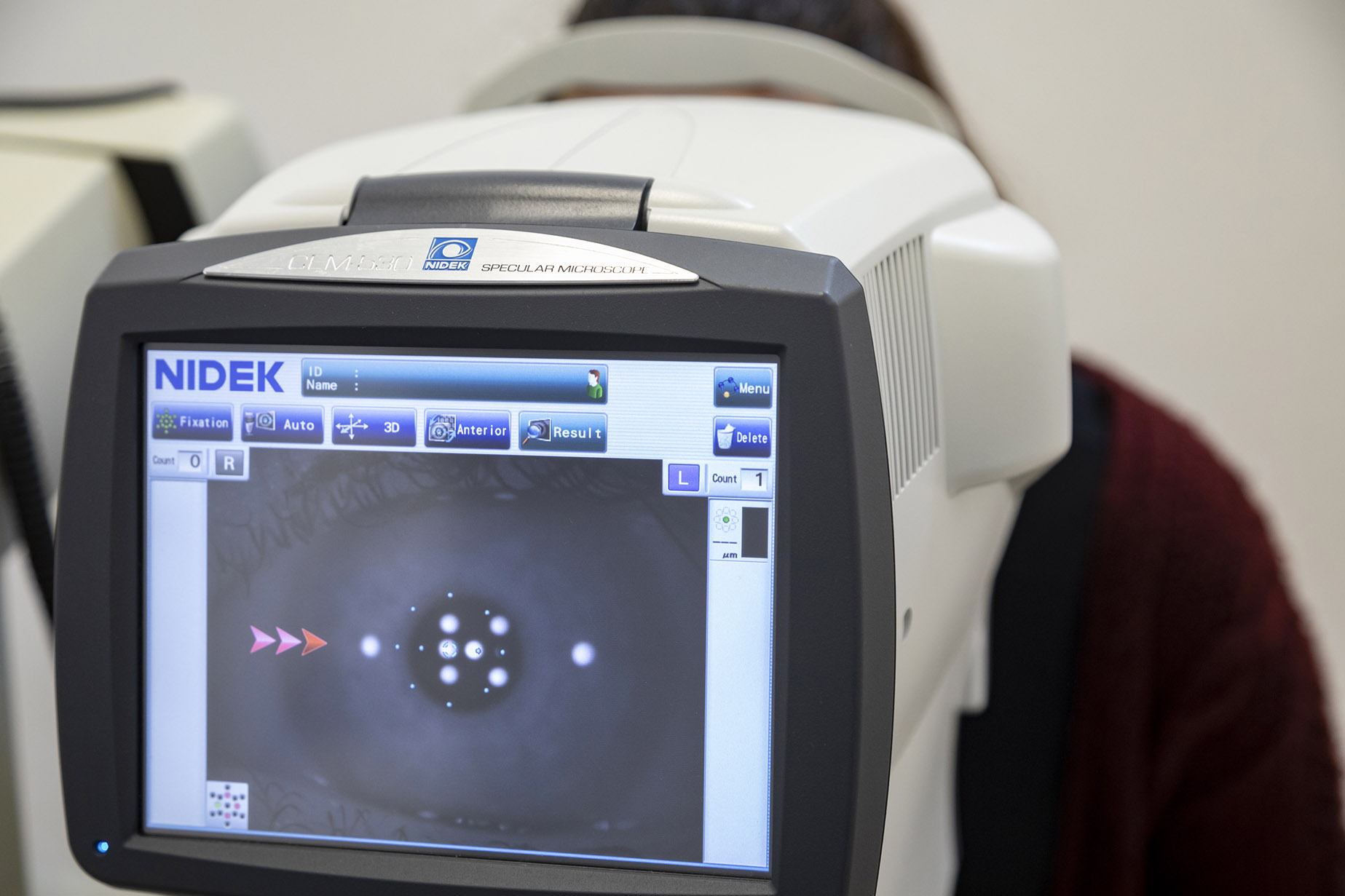
Specular microscopy is a non-contact technique to measure the density and shape of corneal endothelial cells. It is used for the preoperative examination of patients who will undergo cataract surgery or phakic lens implantation.
High resolution ecography of the anterior segment for the study of the cornea, iris, eye lens, ciliary body and angle. It measures diametres, depths, and thickness of the anterior segment structures.
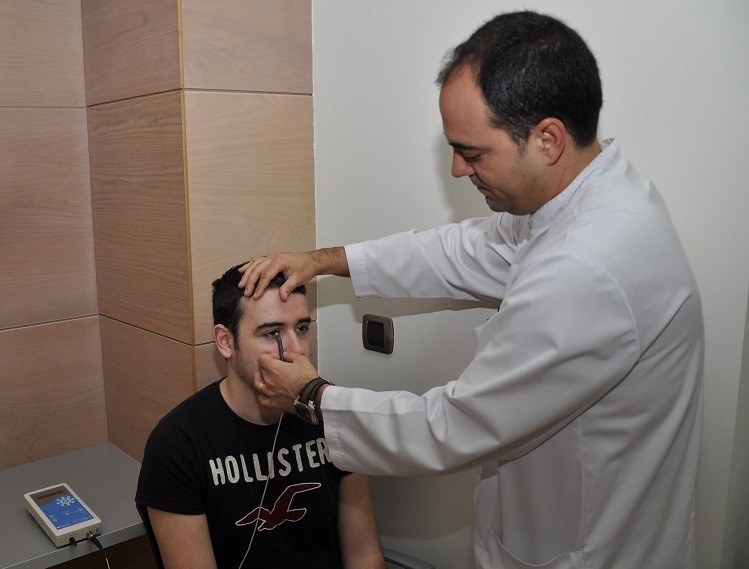
Ultrasonic pachymetry measures the thickness of the corneal structure through ultrasounds. This test is usually used to detect keratoconus and glaucoma and also before performing refractive surgery.
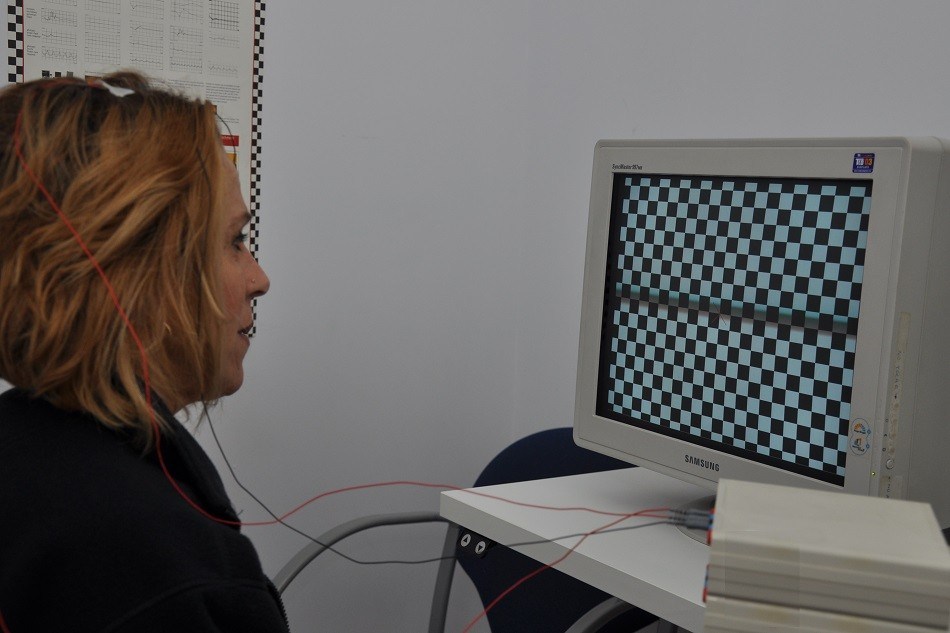

Test to assess the transmission of the electric potentials from the retina to the occipital lobe of the brain. The most frequent application of this study are optic nerve diseases.
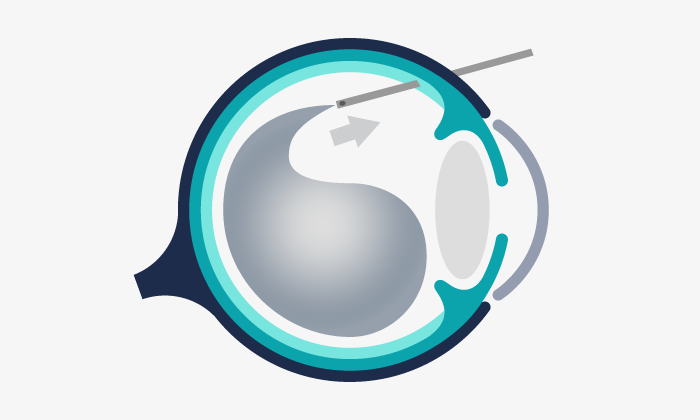
Vitrectomy is a type of eye surgery consisting of the extraction of the vitreous humor fluid. This is usually replaced with a saline solution or with a bubble of gas, air or silicone oil.
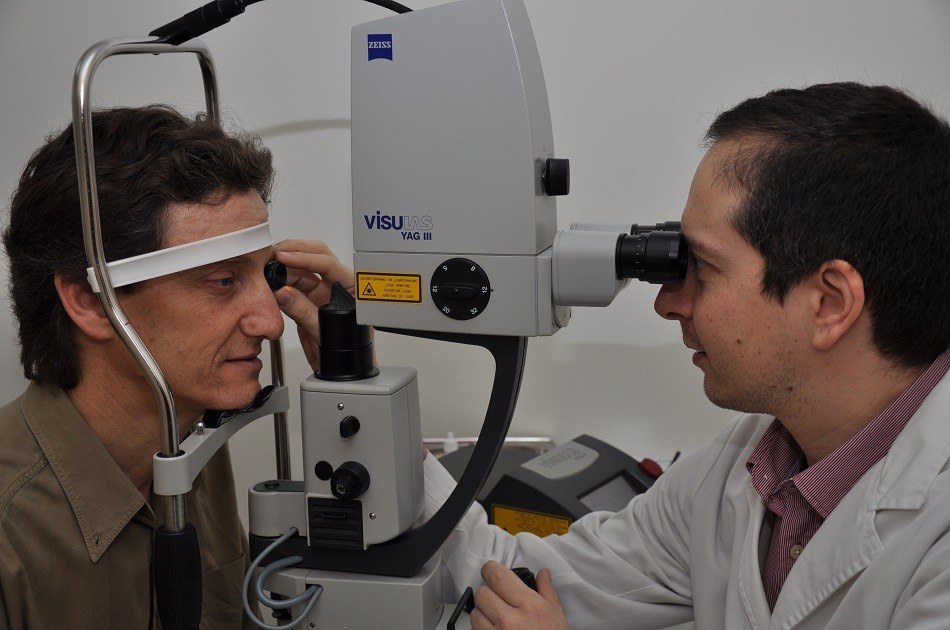
Treatment of the acute angle glaucoma or prophylaxis of narrow angle (iridotomy). It is also used to perform capsulotomies after cataract surgery.
Contact us or request an appointment with our medical team.