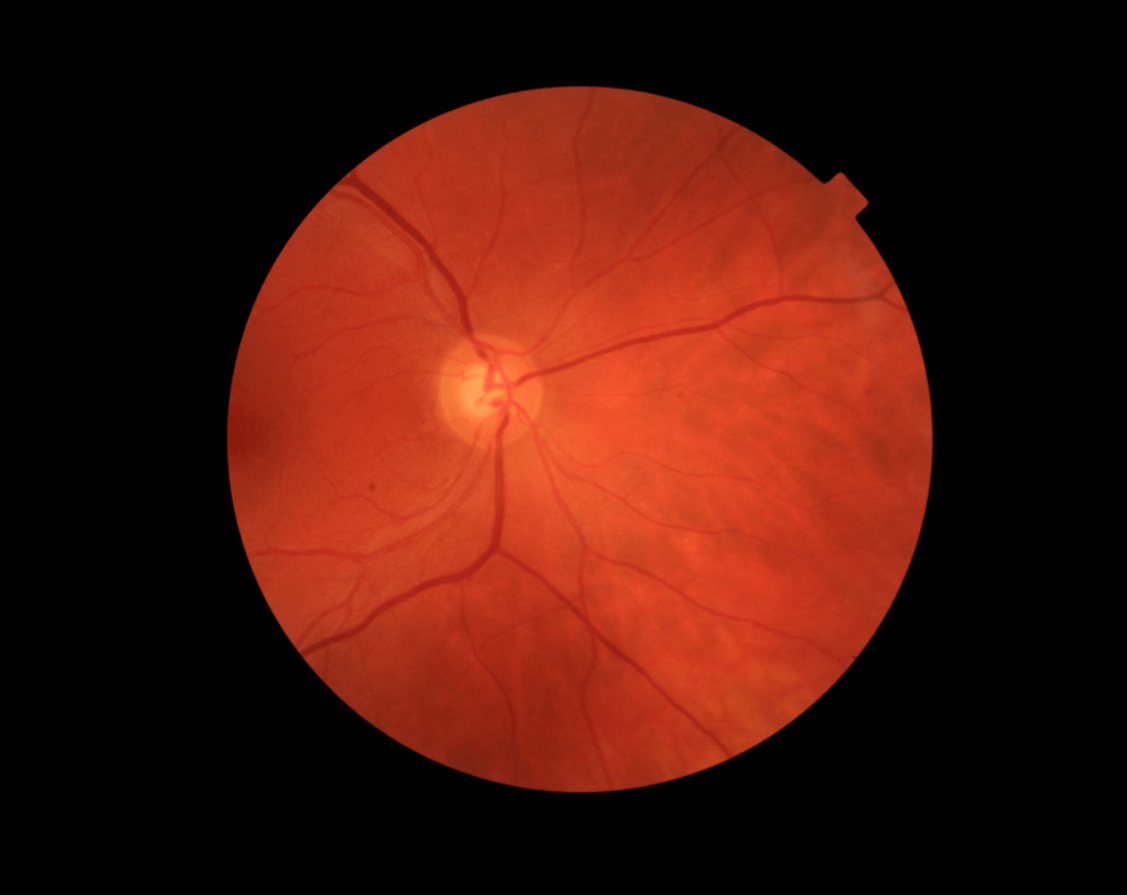
Retinography consists of a digital colour photograph of the retina, that is, the back of the eye. By means of this technique it is possible to identify the blood vessels, record the appearance of the optic nerve of the retina and detect possible changes or findings.
Retinography is a simple and painless test and can be carried out on anyone, regardless of age. It is especially recommended for people over 45 years of age, people with diabetes or hypertension, people with myopia or people with a family history of eye diseases.
This test is used to detect retinal pathologies and to monitor glaucoma. Some of the most common diseases are:
The test does not require any prior preparation. Generally, for the correct realization of the test, pupil dilation is required, which is why 15 minutes before the test is carried out, drops will be given to you at our centre.
The patient must take the test without contact lenses. For this reason, you can come with your contact lenses in place and remove them before taking the test. In this case, you must bring a container to store them.
Due to the action of the drops and the dilation of the pupils, you may see blurred vision at short distances for a few hours, which is why it is advisable not to drive after the test.
The test lasts between 5 and 10 minutes. A microscope connected to a camera that provides a magnified view of the eye is required to carry out the retinography.
Before carrying out the test, the specialist will administer some drops to dilate the pupil. Once this has taken effect, the optometry team will take different photographs of the retina.
The department in charge of carrying out the test is the Optometry Department, which performs all the ophthalmological tests necessary for the diagnosis and supervision of different ocular pathologies and the visual system. The Department has the most advanced diagnostic equipment and the most modern technology, and its 50 optometrists are specifically trained to carry out these tests.
Once the data has been collected, the medical team will be responsible for interpreting the results and transmitting them during the next visit.
The test does not cause any kind of discomfort, as it is a non-invasive technique that does not contact the eye. Likewise, it is possible that you may feel a slight pain at the time of administration of the eyedrops.
Yes, it is recommended that you come accompanied by another person, as after the test you will have blurred vision due to the temporary effect of the eyedrops.
It is not necessary to fast for the test to be performed.
The data are obtained at the same time as the test is taken. If a report from a specialist is required, the informed test will be sent to you within a few days.
No. The optometry department is in charge of performing the test and has the knowledge to confirm that it has been carried out correctly. The ophthalmologist is responsible for interpreting and reporting the results obtained and will do so based on the clinical context after a complete medical history and examination of the patient.
A retinography is a photograph, it does not have normal values. It is an image that reflects the state of the retina and the image responds to the state of the patient’s eye health.
It is advisable not to drive after the test because the effect of the drops can cause blurred vision for a few hours. After the test you can take a shower without any problems.
Widefield retinography is a type of retinography in which a panoramic image of 80% of the retina is captured and can be performed without pupillary dilation. In conventional retinography, images of laser extension are captured and to obtain peripheral images, different captures and pupillary dilation are required prior to the test.
Retinography and OCT are complementary tests used to analyse the retina of the eye. The difference between them is that the former takes a photograph to evaluate the appearance of the retina, while the latter is a virtual scan using a scanner of the structures that make up the retina.
Contact us or request an appointment with one of our specialists.