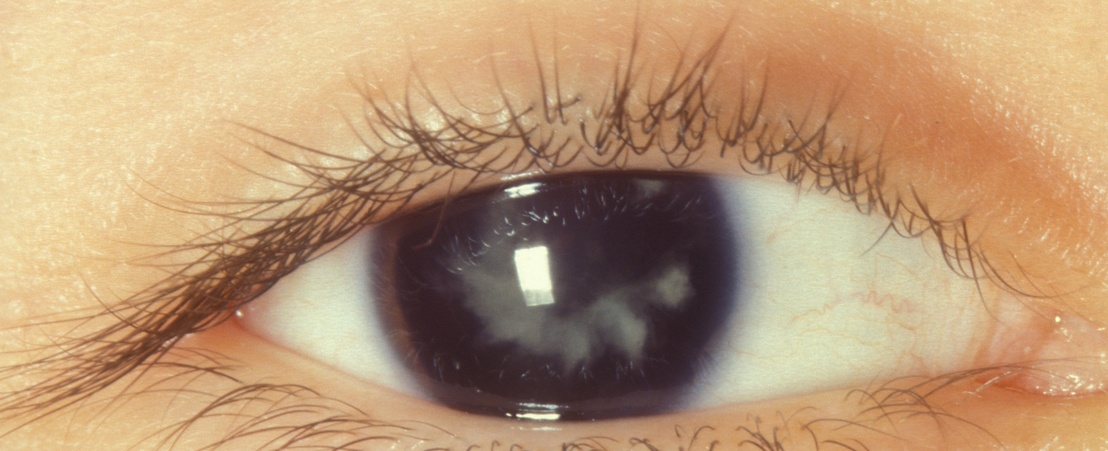
Secondary cataract or after-cataract is an opacification of the posterior capsule of the lens that may appear after a few months or years of having undergone a cataract extraction. This prevents the passage of light to the retina and leads to loss of vision. Up to 20% of patients who have undergone a cataract extraction may suffer from this disorder.
The secondary cataract occurs when there is a proliferation of epithelial cells in the lens of the posterior capsule and the new capsule that supports it. In any case, it is not a reappearance of the cataract that was operated previously.
It is not possible to know if a patient will develop a secondary cataract after the extraction of cataracts. But it is usually developed mainly in younger patients who have undergone a cataract surgery.
If vision problems are noticed after this surgery, you should go to the ophthalmologist to perform an ophthalmological assessment.
Secondary cataract is associated with symptoms similar to primary cataract, such as:
The treatment that is usually recommended after the appearance of a secondary cataract is to undergo a capsulotomy.
The capsulotomy consists of making an incision in the posterior capsule with the help of the Nd:YAG laser. The ophthalmologist will use eye drops to dilate the eye and, once the pupil is dilated, you should place the head on the laser.
The ophthalmologist will place the laser on the back of the capsule to cut a small area and remove part of the cells to allow light to enter directly through the retina.
In any case, the ophthalmologist will assess the need to perform this intervention based on the visual deterioration of the patient and his medical history, in order to avoid associated risks.
The intervention with Nd:YAG laser is usually a quick and painless operation that is performed on an outpatient basis and, therefore, the patient can leave the center after performing the surgery. Nevertheless, it will be necessary to perform controls if specified by the ophthalmologist.
It is possible that, during the following days, you may notice that the vision is not yet fully recovered and that you may notice blurred vision. In case of seeing eye floaters, flashing lights or a dark curtain that moves up and down or sideways, you should go urgently to the ophthalmologist to dismiss associated risks.

Contact us or request an appointment with our medical team.