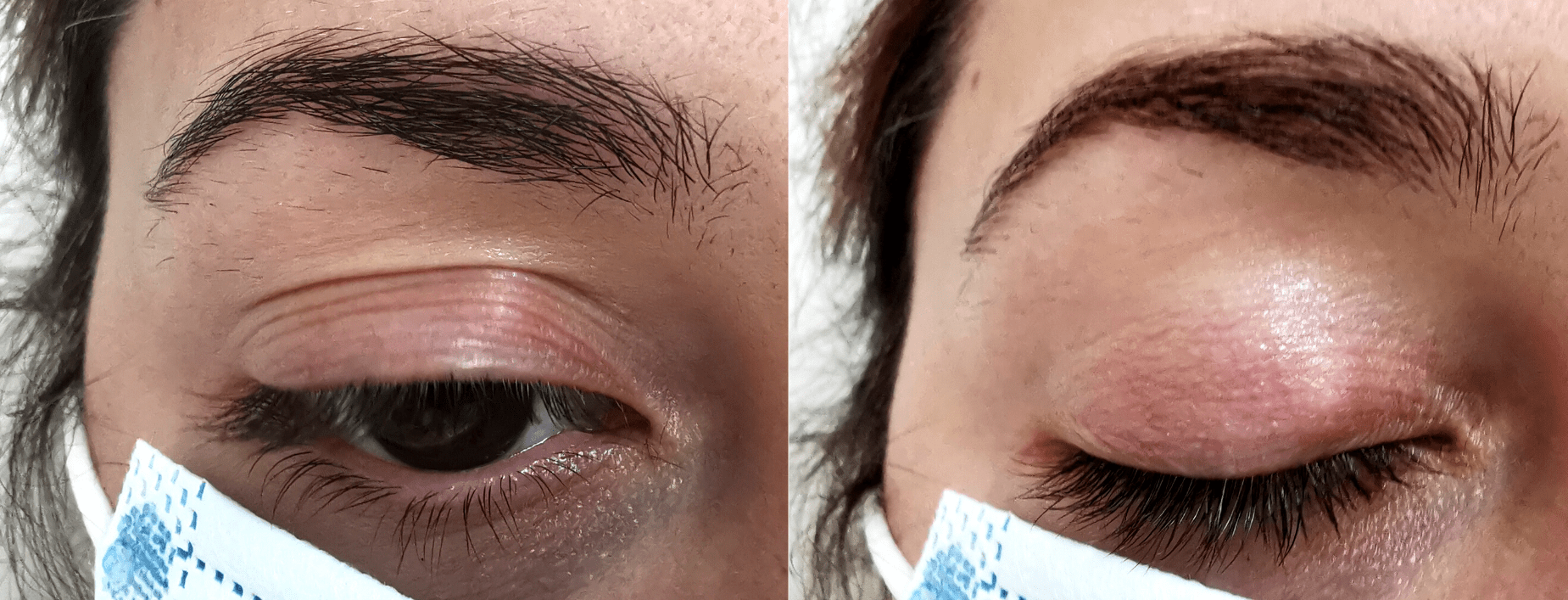
A chalation or chalazion is a benign pump or lump in the eyelid that does not cause pain and appears when secretions from the Meibomian glands accumulate due to a blockage in the drainage of the glands. In those cases the secretion is retained inside, which makes this nodule appear.
Usually, the chalation is not painful, but if its size grows it can become annoying, and put pressure on the eye, causing astigmatism and blurred vision. When it becomes infected and inflamed, we speak of a stye.
The Meibomian glands are located inside the eyelid and produce an oily secretion that is part of the tear film. When the drainage openings of these glands are obstructed, the secretion does not drain and accumulates, forming a fatty cyst called a chalation.
The chalation is usually common in people suffering from blepharitis, seborrheic or rosaceae dermatitis, and in people with a history of stye.
The common symptoms associated with a chalation are:
It is always recommended to consult an ophthalmologist at the onset of any symptoms.
Sometimes it is not necessary to treat, since the chalation disappears by itself after a few days. In cases where the chalation does not resolve spontaneously, the following treatments may be used:
To prevent the development of a chalation, it is important to maintain good palpebral hygiene, especially for people who have a history of blepharitis.
The inner area of the eyelids, the palpebral edge, and the eyelashes should be cleaned with special eye hygiene wipes or soaps, especially if makeup is used on that area.
Likewise, it is also recommended to follow a diet rich in Omega 3 fatty acids due to their anti-inflammatory properties.
As part of the initial treatment, hot compresses infused with chamomile can be used to locally massage the affected area.
The use of other home remedies that are not indicated by your ophthalmologist is not recommended.
The hygiene of the palpebral edge and the eyelashes should be carried out with wipes or specific soaps for ophthalmic use indicated by your ophthalmologist.
It is not recommended. It is suggested to avoid products that are applied to the eyelashes and palpebral edge, such as mascara or eyeliners, since they promote the obstruction of the Meibomian glands.
No. You must always go to your ophthalmologist to avoid unnecessary manipulations that can favor infections and worsen inflammation.
Contact us or request an appointment with our medical team.