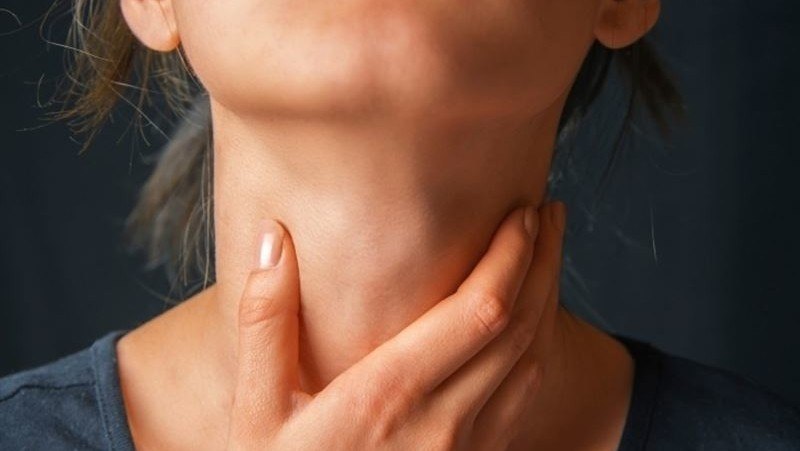
Thyroid orbitopathy, also known as thyroid ophthalmopathy, is an affectation of the periocular tissues that is associated with autoimmune diseases of the thyroid gland, such as hyperthyroidism. However, this pathology can also appear in people with hypothyroidism and even without apparent thyroid condition. Although the main affected organ is the thyroid, it is also common to cause alterations in the orbital tissues. This disease affects mostly adult women and is associated with smoking.
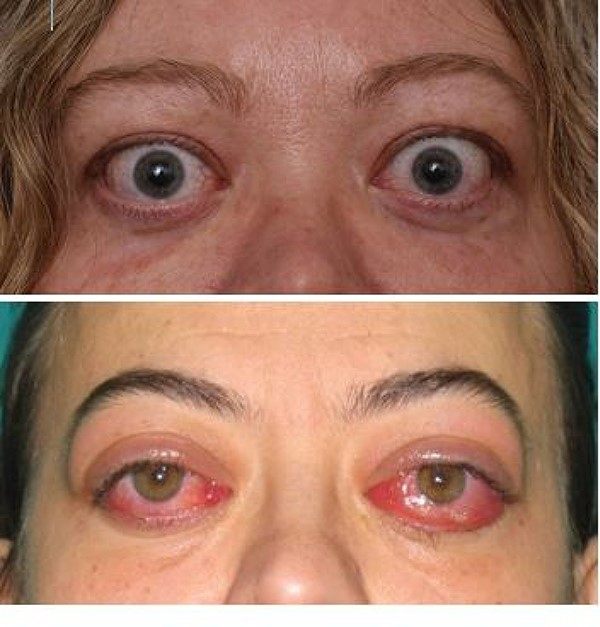
Thyroid orbitopathy is caused by a malfunctioning of the thyroid gland, causing affections in the eyelids, the orbit and the periocular muscles, as well as an increase in the volume of orbital fat resulting in bulging eyes, exophthalmos or proptosis.
Patients with hyperthyroidism are more likely to suffer from thyroid orbitopathy. In hyperthyroidism, the body produces an abundance of antibodies and causes an excess of hormones from the thyroid gland. This overproduction affects the soft tissues of the orbit, which become inflamed as a result.
The symptoms of OT are varied, from mild discomfort to blindness caused by a corneal ulcer. In addition, the symptoms are more pronounced in the morning. The symptoms related to the disease are:
The treatment in thyroid orbitopathy can vary depending on the symptoms that are manifested and the time spent with the pathology.
In cases of patients suffering from mild O.T., without double vision or corneal ulcers, a conservative treatment of the cornea is usually performed by ocular lubrication, to protect it from drying out by exposure, and a systemic treatment with oral selenium to stop the inflammatory process of the disease.
When there is a progression of the disease and the symptoms begin to affect vision, the treatment used is anti-inflammatory, specifically intravenous methylprednisolone. In the most severe cases, the inflammation can lead to fibrosis and affect the orbital muscles and fat causing permanent sequels that will require treatment with surgery to improve the symptoms and appearance of the eyelids.
In cases where there is no response to medical treatments and there is a risk of permanent vision loss or the effects are very important such as large exophthalmos or corneal ulcers that affect vision the treatment required is surgery by orbital decompression to correct proptosis or bulging eyes.
In cases of patients who smoke, it is very important to stop smoking so that the OT gets better.
There is only one type of thyroid orbitopathy that is classified according to its activity, active or inactive, and its severity, mild, moderate or severe.
OT is not entirely preventable, but good control of systemic disease (hyperthyroidism) by the endocrinologist and not smoking or quitting before it appears can prevent the disease from manifesting itself or from becoming milder. Also, an early diagnosis of the disease can allow better control and early detection of problems, so that complications can be avoided.
The diagnosis of OT is made through an initial physical examination, along with a complete ophthalmological examination (it is a clinical diagnosis) and a blood test to determine the function of the thyroid gland. Sometimes the diagnosis is complemented with a CAT scan or an MRI, in order to detect all the affectations that the patient presents.
Although patients with OT may suffer more frequently from an increased eye pressure, no correlation has been proven between thyroid orbitopathy and the appearance of glaucoma.
OT can occur in only one eye, although in 90% of cases it occurs in both eyes. However, the affectation is usually asymmetric, so one eye may be more affected than the other.
Traditionally, OT was treated with radiotherapy, although it is currently being dropped in favor of other more effective and safe treatments such as immunoglobulins.

Contact us or request an appointment with our medical team.