Corneal dystrophies are a group of genetic disorders most often found in the cornea (the clear front surface of the eye that lies directly in front of the iris and pupil and when it’s healthy, is like a transparent crystal).
Fortunately, most of them are disorders without any visual consequence and therefore of a a slight severity. However, in other cases it may lead to the need to perform a corneal transplant. In corneal dystrophies, an alteration occurs in one of the 5 layers of the cornea. The affectation of these can go from a slight upheaval in the adhesion of the layers, happening through an accumulation of abnormal way of certain material (normally in the middle layer of the cornea), until a deficit of the number of cells that cover the cornea by the internal part. Most corneal dystrophies affect both eyes, progress slowly and generally slowly, and are transmitted genetically.
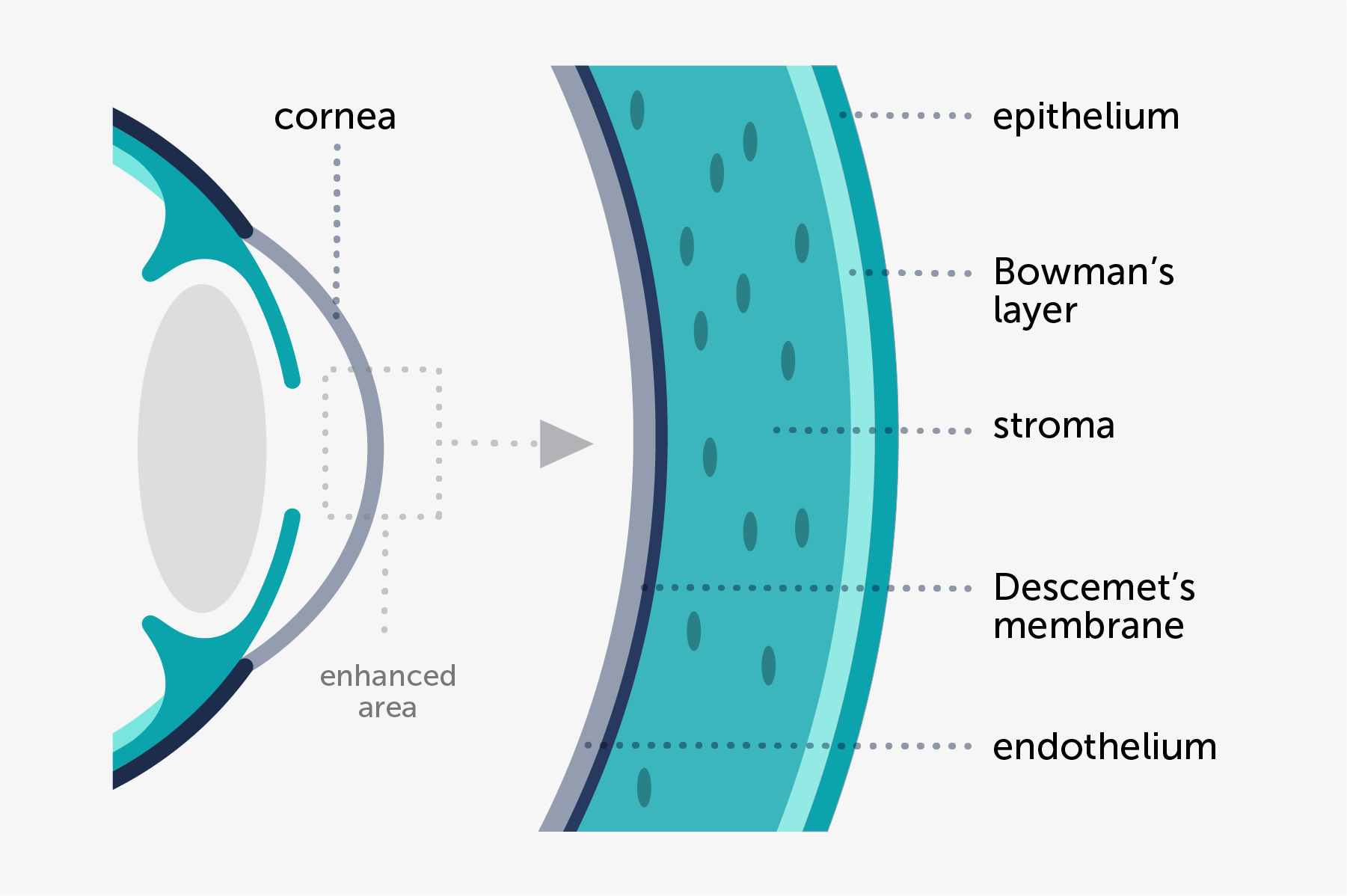
The cornea has five layers. From front to back, these layers are:
The corneal epithelium : the outer and protective layer of the cornea
Bowman’s layer: a second protective and resistant layer
The corneal stroma: the thickest layer of the cornea, composed of water, collagen fibers and other connective tissues that strengthen this structure and make it transparent and flexible
Descemet’s membrane: intern protective layer.
The corneal endothelium: the innermost layer of the cornea composed of cells that pump excess water out of the cornea.
There are more than 20 different types of corneal dystrophies, which are usually grouped into three categories, depending on the layer of the cornea that is affected.
Anterior or superficial corneal dystrophies: affects the outermost layers of the cornea: the epithelium and Bowman’s membrane.
Stromal corneal dystrophies: They affect the stroma, the middle and thickest layer of the cornea.
Posterior corneal dystrophies: affect the innermost areas of the cornea: the endothelium and the Descemet membrane. The most common is Fuchs’ dystrophy.
The treatment of corneal dystrophy will depend on the type and severity of its symptoms. In the absence of symptoms, the ophthalmologist will control the disease to see if it evolves. In other cases, it may be necessary to administer drops, ointments or even laser treatments.
Many people affected by corneal dystrophy will suffer corneal erosions repeatedly. This type of involvement can be treated with antibiotics, lubricating drops, ointments or special soft contact lenses to protect the cornea. If erosion persists, other therapeutic options can be assessed, such as the use of laser therapy or a corneal scraping technique.In more severe cases, a corneal transplant (or keratoplasty) may be necessary, whereby damaged or diseased corneal tissue is replaced by healthy corneal tissue from a donor.
Today we are performing partial cornea transplants, so we are able to replace only the damaged part of the cornea and preserve the rest if it is healthy. This minimizes the risks, both operative and of a later rejection, in addition to accelerating visual recovery. In the case of endothelial dystrophies (such as Fuchs’), a partial transplant is performed only on the posterior layer (or endothelial keratoplasty).Corneal transplants, despite being in the last therapeutic step, have proven to be a very beneficial procedure in patients with low vision, whose corneas are considerably damaged by corneal dystrophy.
Contact us or request an appointment with our medical team.