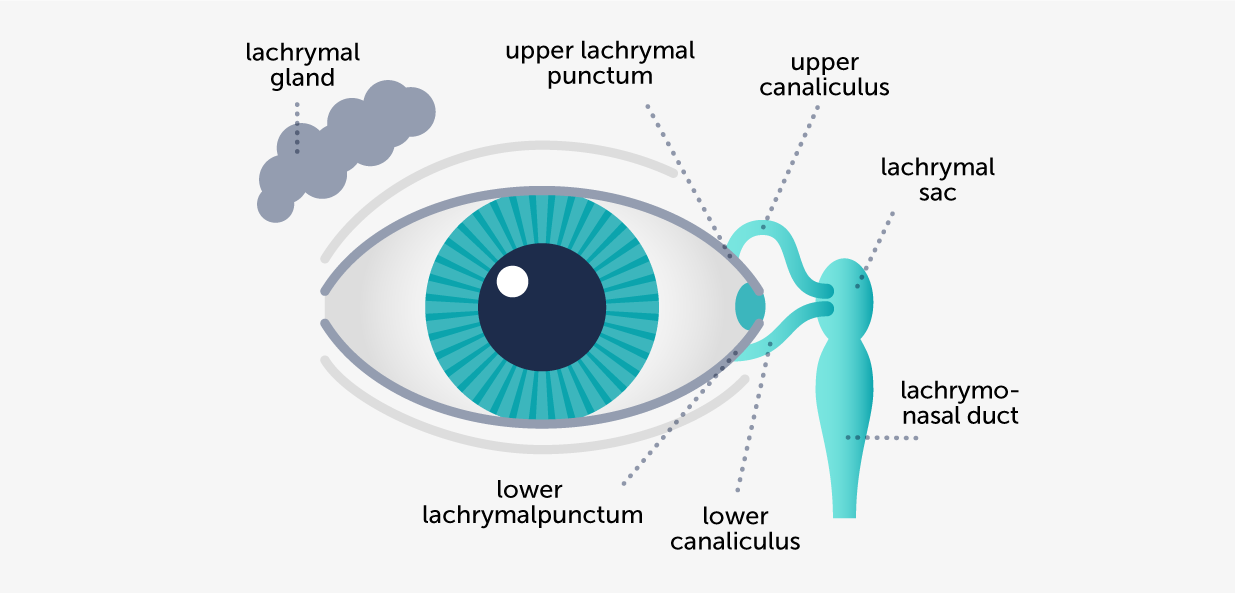
Dacryocystitis is an inflammation usually caused by a lachrymal sac infection, arising from an obstruction of the tear duct.
Pain, redness and edema at the level of the internal side of the lower eyelid (under the lachrymal sac), tearing, discharges, occasional or recurrent fever.
Painful and erythematous edema located in the level of the nasal side of the lower eyelid, spreading towards the area of nasal periorbit. When pressure is put on the lachrymal sac, mucous or purulent discharges may go out through the lachrymal punctum.
Other signs are the creation of a fistula (usually with emergency point at the level of the medial canthal tendon) or a cyst in the lachrymal sac or mucocele, especially in chronic cases. There are rarely complications such as orbital or facial cellulitis.
The most common cause is the obstruction of nasolachrymal duct, although less frequently it can be caused by other conditions, such as face trauma, previous nose surgery or tumours.
It depends on the symptoms degree of gravity and the signs found during the exploration performed by the specialist. It requires a comprehensive ophthalmology examination and, when possible, the obtainment of a culture of any secretion extracted from lachrymal punctum.

Contact us or request an appointment with our medical team.