
Astigmatism is a defect in the curvature of the cornea (the dome-like transparent structure which covers the iris and the pupil) or in the shape of the eye lens.
Normally, the cornea and the lens are regular and are curved in the same shape throughout. This helps to focus light clearly onto the retina at the back of the eye. Nevertheless, if the cornea or the lens are not smooth or do not have a regular curve, the rays of light do not refract correctly, which causes a refraction problem.
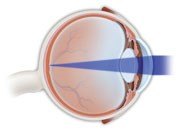
In a normal eye, the cornea and the lens focus the light onto the retina.
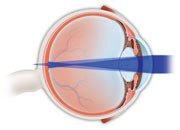
In an astigmatic eye, the images get focused either in front of or behind the retina, which means that the images appear blurred.
Corneal astigmatism is when the cornea has an irregular shape. This is the more frequent type.
Nevertheless, there is also astigmatism of the lens in which case it is the lens that is deformed. Both cause near and far objects to appear blurred and distorted.
Some people are born with this defect. In fact, the majority have a certain degree of astigmatism that may be combined with other refraction defects, such as myopia or hypermetropia.
Adults with a high degree of astigmatism may realize that something is wrong with their vision due to blurred or distorted vision, visual fatigue, headaches, the need to squint to focus better or other visual problems which, although not necessarily indicating the presence of this refraction defect, do indicate the need to visit the ophthalmologist for a check-up.
In the case of children, they may not realize that they are suffering from this refractive defect, and may not complain of blurred or distorted vision. Nevertheless, if it goes uncorrected, it may affect the child’s performance at school. This is why it is essential that they see the ophthalmologist.
Normally, low to medium prescriptions can be corrected with glasses or contact lenses (soft or hard). In cases of higher prescriptions, glasses or hard contact lenses are normally more suitable, but this will depend on each specific case.
On the other hand, for some with this refractive defect, various surgical techniques may be an option for correcting their vision.
Contact us or request an appointment with our medical team.