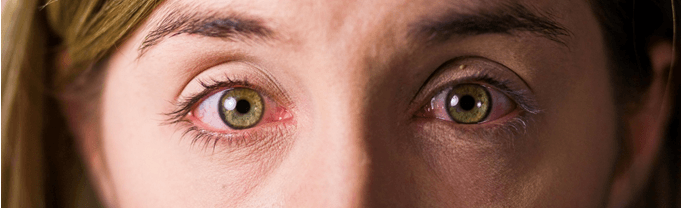
Endophthalmitis means the presence of an intraocular bacterium or fungus that causes an infection of the intraocular fluids.
Any type of surgery can be complicated by endophthalmitis. However, the most common, since it is one of the most frequently performed surgeries, is cataract surgery. However, any surgical intervention could cause endophthalmitis.
Recently, a higher number of cases are observed in patients receiving intravitreal injections, either for the treatment of macular pathology in diabetics or age-related macular degeneration.
Glaucoma surgery can also be complicated, and not only in the initial stages or in the immediate postoperative period, but also long after the operation.
It can also occur in vitrectomies, a surgery that is performed for retinal detachment or in other types of intraocular surgeries could also become complicated.
*Normally, the frequency or incidence of cataract surgery is 1 per 1,000 patients operated on.
Symptoms will depend on the type of endophthalmitis and its severity. Typically, a patient who has had cataract surgery will present with vision loss, red eye and/or pain.
Patients with endogenous endophthalmitis usually do not present with pain and inflammation or erythema (eye redness) may present at later stages. These patients usually come to the center with loss of vision and/or presence of myodesopsia or floaters.
The diagnosis of endophthalmitis is primarily clinical. This means that the ophthalmologist will have to suspect this complication, usually in a patient presenting with typical symptoms and a history of intraocular surgery. It is more complex when this is not present and endogenous endophthalmitis is suspected. In any case, samples should be taken from the eye and this is done in an operating room.
One of the ways is to aspirate this gelatin, the vitreous humor and the aqueous humor, or to perform a vitrectomy.
The treatment of endophthalmitis has to be as urgent as possible and consists of the administration of antibiotics or antifungals directly into the eye and, in those cases where there is a severe inflammatory reaction, corticosteroids are also administered orally.
In some cases a surgical intervention such as vitrectomy will be necessary to free the intraocular cavity from this associated inflammatory and infectious reaction.
The visual prognosis of endophthalmitis is still considered guarded. It depends very much on the type of agent and the characteristics of the eye or the cause of this infection. For example, patients with very poor visual acuity have a more guarded prognosis, as well as older patients.
However, with the development of new surgical and diagnostic technologies and the improvement of different antimicrobial agents, the prognosis of endophthalmitis, for example, after cataract surgery, is not as bleak as it was a few years ago and patients can normally achieve a visual acuity of 50% of the acuity they had previously.
Contact us or request an appointment with our medical team.