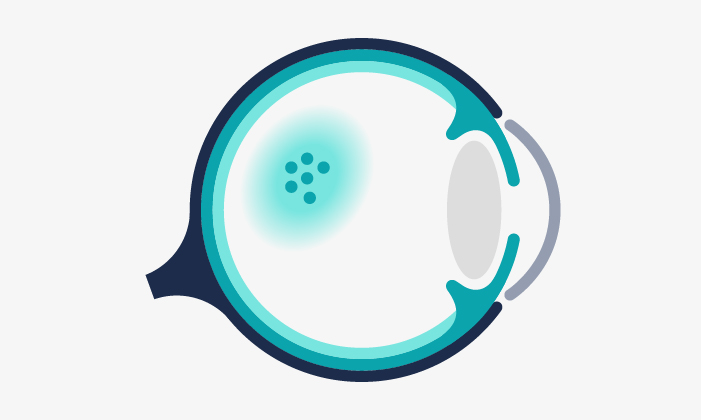

AMD it is a pathology that affects the central vision. It progresses as the patient’s age increases and can lead to blindness if not treated early.

Age-related distance esotropia is the loss of paralelism between the shafts of the eyes and the target fixation, produced in adults over 65 years old.

Allergic conjunctivitis is an inflammation of the conjunctiva caused by a reaction to an allergen (any substance that produces an allergic reaction).

Amblyopia or lazy eye is a vision alteration caused by an asymmetry in the position of the eyes. It usually develops at a very early age and is the leading cause of childhood vision loss.

Astigmatism is a defect in the curvature of the cornea or in the shape of the lens of the eye that can be solved with glasses or with refractive surgery.
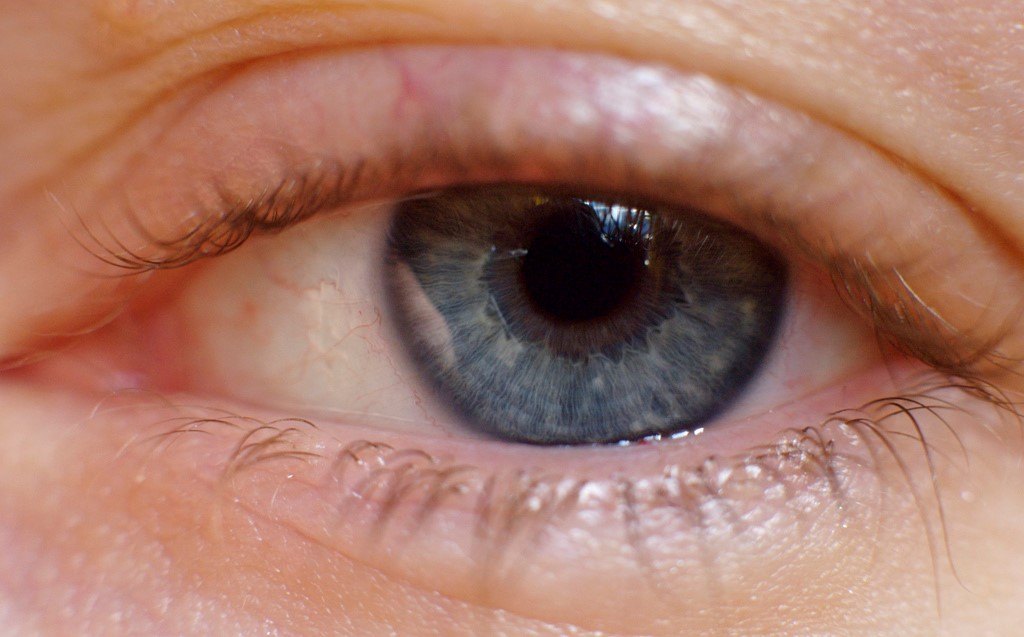
Blepharitis is an inflammation that occurs at the edge of the eyelids causing redness, peeling and swelling of the eyelids. It is usually chronic but it does not usually cause permanent damage.
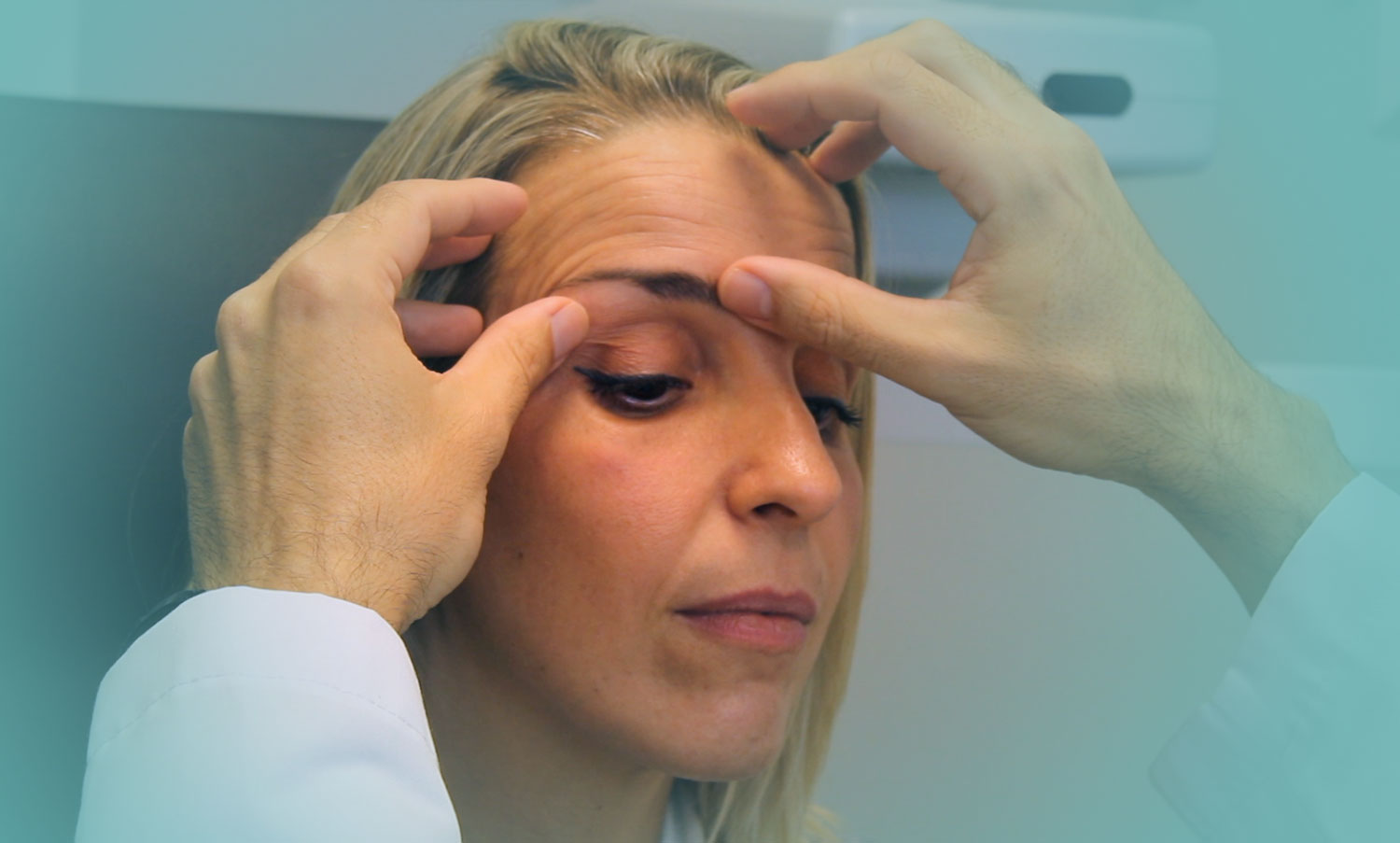
Blepharoplasty is a minimally invasive operation that removes excess skin, and sometimes fat, from the eyelids. With this surgery it is possible to improve the tired aspect of the face.
Thanks to the latest innovations in intraocular lenses, we can regain the vision lost due to cataracts and reduce the dependency on glasses at the same time.

Central serous chorioretinopathy is the fourth retinal disease that threats our vision, behind age-related macular degeneration, vascular occlusions or diabetic macular edema.
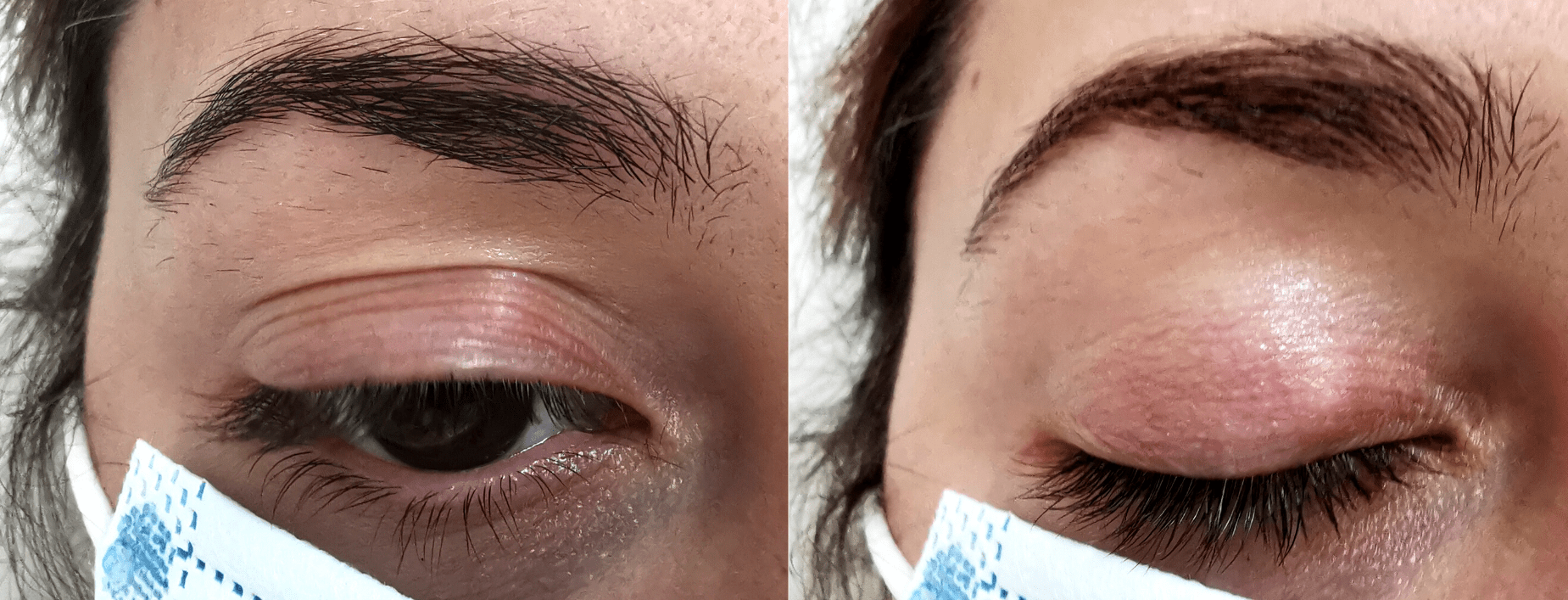
A chalation or chalazion is a benign pump or lump in the eyelid that does not cause pain and appears when secretions from the Meibomian glands accumulate due to a blockage in the drainage of the glands.

Childhood myopia is the refractive defect that causes blurred vision for objects that are far away, affecting children. It is usually treated with prescription glasses.

Coats disease is characterized by
a unilateral and anomalous development of the retina’s blood vessels. It is usually diagnosed in male patients during the first two decacdes of the patient’s life.
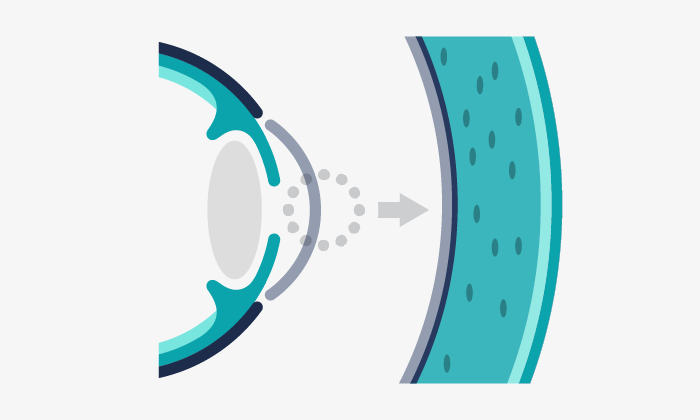
Conjunctivitis is the inflammation of the conjunctiva, the mucous membrane that covers the inner part of the eyelids in the anterior part of the eye, touching the cornea.
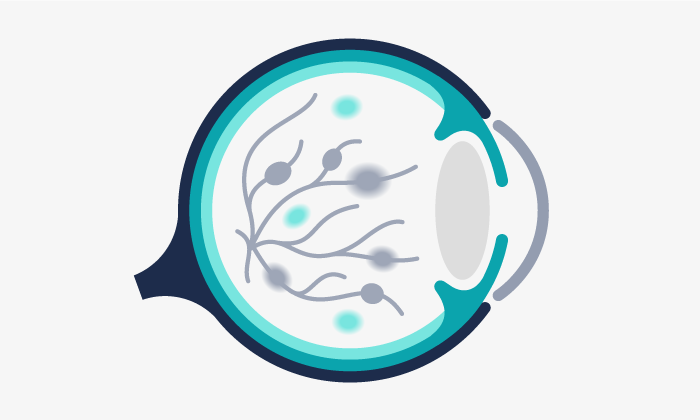
Corneal dystrophies are a group of genetic disorders most often found in the cornea (the clear front surface of the eye that lies directly in front of the iris and pupil).

A corneal ulcer is an open wound on the cornea, the structure that covers the iris and the pupil in a similar way to the crystal covers a watch face.

A corneal laceration is a cut in the cornea, usually caused by the contact of some sharp object with the eye, whereas a corneal abrasion is a scratch on the cornea usually superficial and does not leave a scar.

Dacryocystitis is an inflammation usually caused by a lachrymal sac infection, arising from an obstruction of the tear duct. It can cause symptoms such as pain, redness and edema.
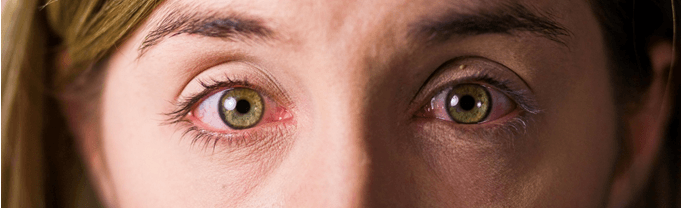
Diabetic retinopathy is a vascular disease secondary to diabetes. Diabetes damages the small blood vessels of the retina due to the metabolic decompensation that it causes.

Diplopia is a visual alteration consisting in the perception of double vision. This vision disturbance can be horizontal, vertical or oblique depending on how the images appear.

Dryness, inconvenience, stinging or a feeling of sand in the eye could be symptoms of dry eye syndrome and require personalized treatment.

An ectropion is an eyelid malposition consisting in the outward folding of the eyelid so it does not sufficiently rest on the eye, thus leaving it exposed and unprotected.
Endophthalmitis is the presence of intraocular bacteria or fungi that causes the infection of intraocular fluids. Treatment has to bee urgent wiith the administration of antibiotics or antifungals.

What is an entropion? An entropion is the inward folding of the eyelid, that makes the eyelashes rub against the cornea, thus leading to eye irritation and redness.

Eye cosmetic treatments are procedures from an ophthalmological specialization focused on correcting and improving the looks of the patients’ gaze.
Eyelid tumors are those that appear in the eyelids in the form of small injuries or lumps that usually don’t cause symptoms, whereas orbital tumors are located in the orbital cavity that surrounds the eye.

Eyelid malpositions are defects in eyelid position that usually appear later in life. An eyelid rolled inward leads to an entropion, while an eyelid rolled outward causes an ectropion.

Eyelid tremors are very common amongst the population. Myokymias are benign and usually temporary, whereas blepharosmasms should be looked into, diagnosed and treated by neuroophthalmologists.
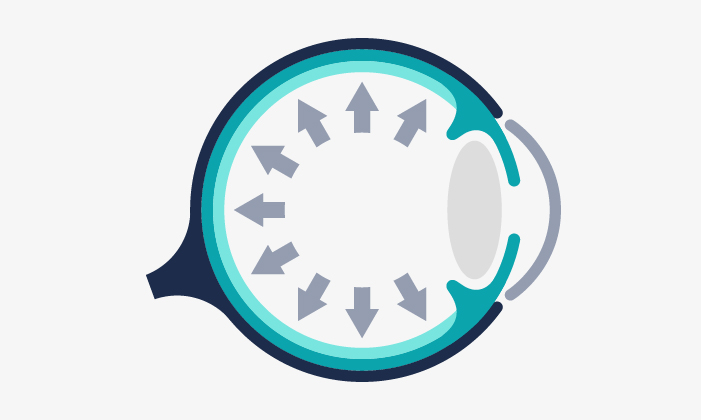
Glaucoma entails a loss of the vision field, usually asymptomatic until later stages of the disease. If it is not treated properly, it can induce blindness.

We speak of high myopia when a patient has more than 6 diopters. This type of myopia is associated with even longer eyes, that is, with a very long axial length.

Hyperopia, hypermetropia or farsightedness in children appears as a refractive defect whereby the image is focused behind the retina and vision is blurred.

Hyperopia is a defect in the eye’s refraction that occurs when images are focused behind the retina and not directly on it, resulting in blurred or unclear vision at intermediate and close distances.
Hypertensive retinopathy is a condition in which the blood vessels in the eye are damaged as a result of high blood pressure. If left untreated, this can seriously threaten vision.

Infectious conjunctivitis is caused by an infectious agent (bacteria or virus) and usually manifests itself acutely. Symptoms and treatment may vary for different kinds of conjunctivitis.

Inhereted retinal disorders (IRD) are a group of retinal diseases of genetic origin that affect 2.5 million people worldwide.
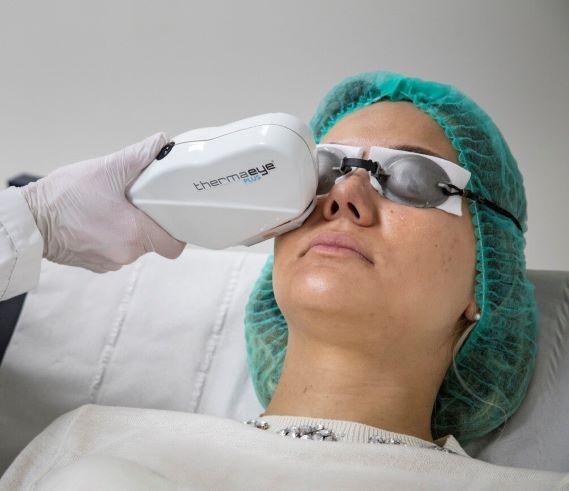
Intense pulsed light is an innovative treatment for dry eye syndrome. It is indicated in cases of Meibomian gland disorders.
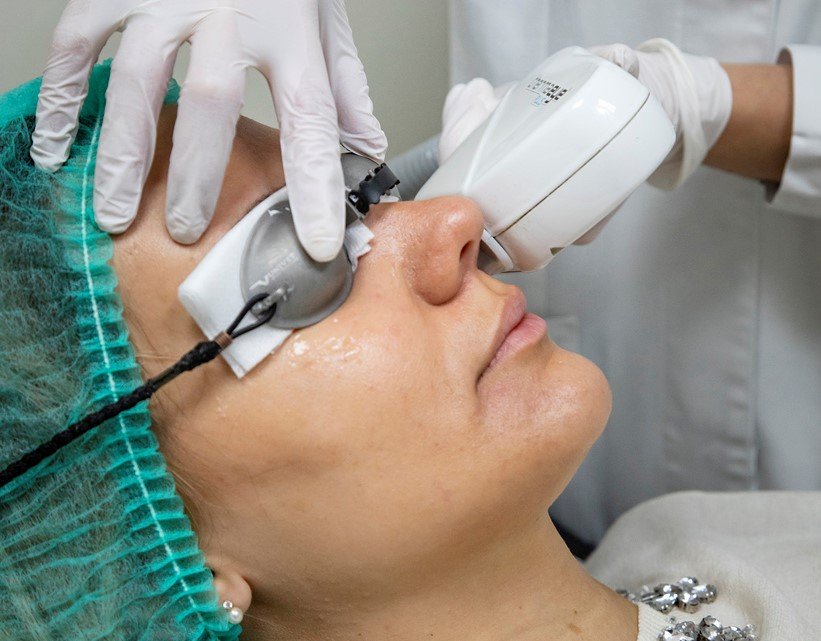
IPL treatment can individually address a variety of skin imperfections and significantly improve its appearance.

Macular degenerations are retinal diseases of genetic origin that cause an early degeneration of the macula that affect adults, young people and children.
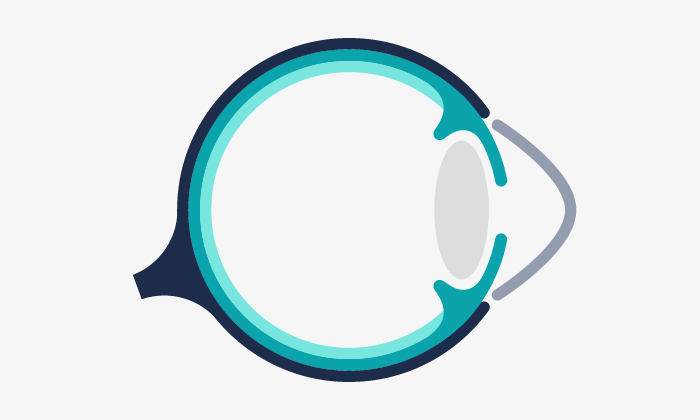

Keratoconus appears when the corneal tissue deteriorates, modifying its usual spherical shape by a cone shape. As the shape of the cornea is altered, the vision becomes distorted.
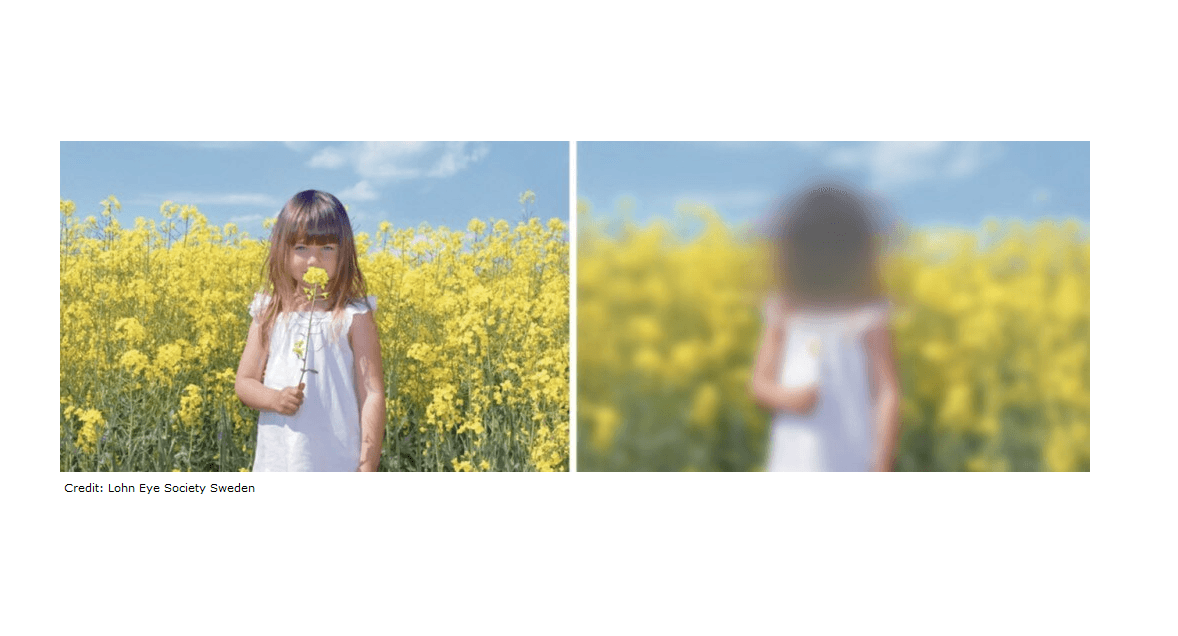

Leber Hereditary Optic Neuropathy (LHON) is the most common hereditary optic neuropathy and causes sudden vision loss mostly among men aged 15 to 25 years old.
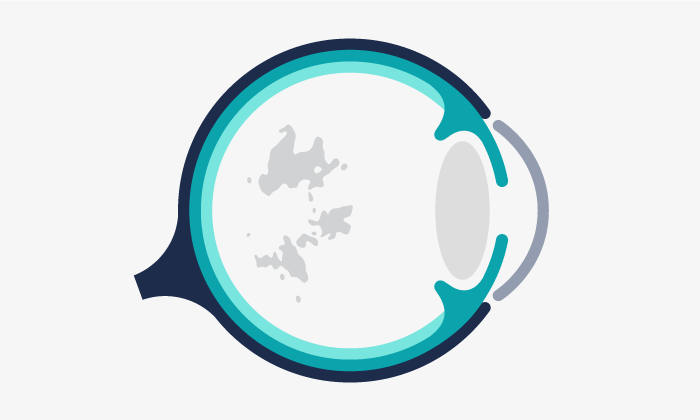

Macular edema is the inflammation or enlargement of the macula, the part in the eye that is in charge of central vision and allows to percieve details.
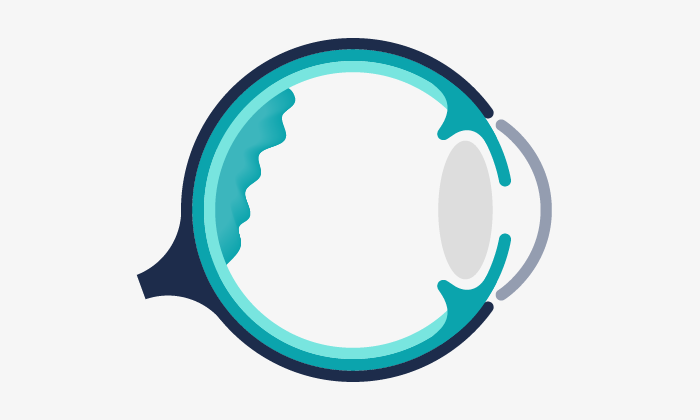

Macular epiretinal membrane causes a slow and progressive visual loss lasting months or years, and affecting one or both eyes. Generally, it causes image distortion, and undulation of straight lines.

A macular hole causes loss of central vision and distortion in the images and is manifested with undulation of straight lines. There are several surgical procedures that can be performed to treat it.
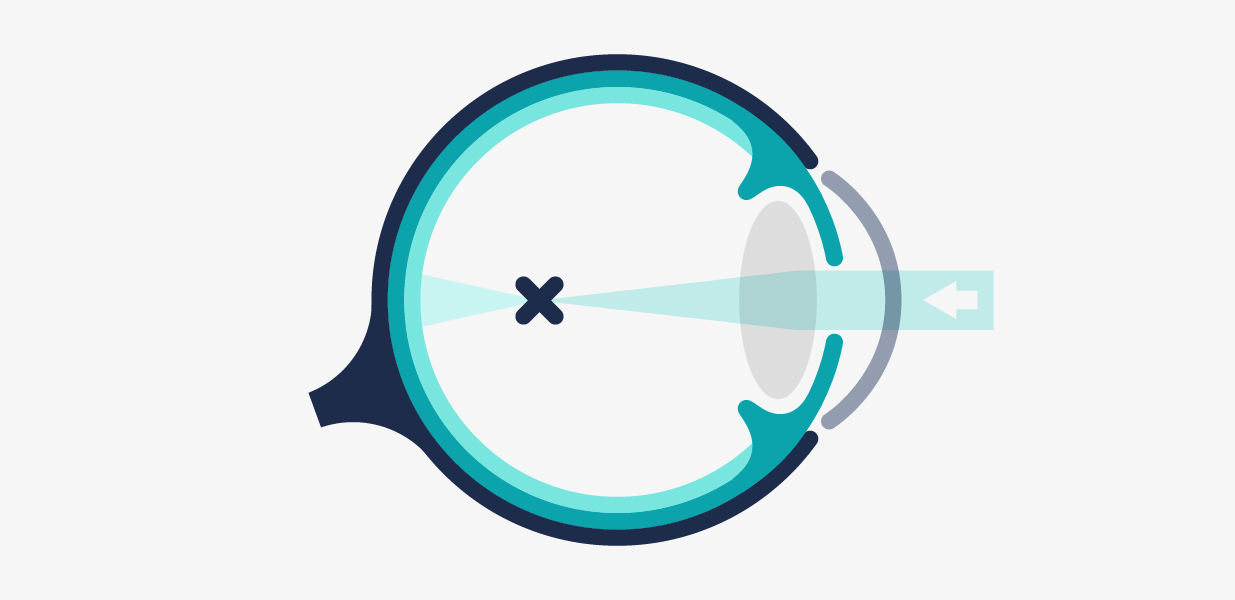

Myopia (near-sightedness or short-sightedness) is a visual defect suffered by myopic or short-sighted people, who can clearly see close objects, but can’t properly focus far distance ones.
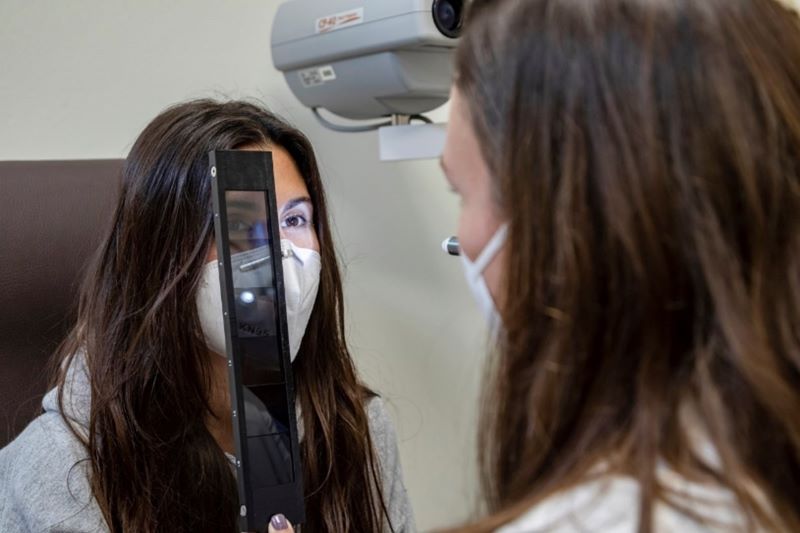
Neuro-ophthalmology treats diseases that, without being properly of the eyes, manifest themselves with alterations of vision, eye movement or pupils. The patient sees badly but the cause is in the brain, optic nerve or elsewhere in the body.
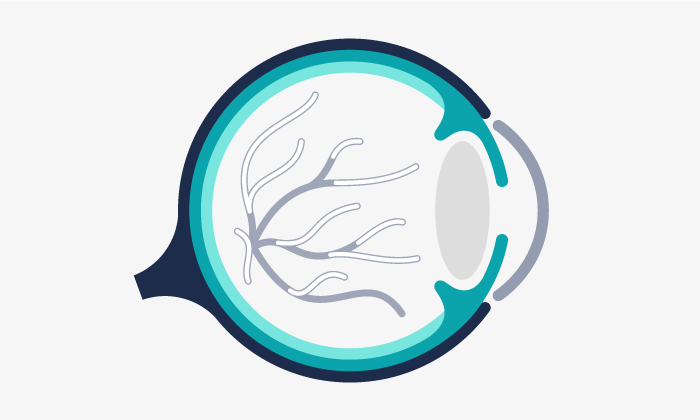
Occlusions or obstructions of veins and arteries in the retina are impediments of the blood flow that cause ischemia or flooding. It can cause a painless vision loss to either the entire visual field or only a part of it.

Optic neuritis is an inflammation of the optical nerve. This inflammation may be located at the nerve’s front side (papillitis) or at the rear side of it (retrobulbar optic neuritis).

Orbital cellulitis is a serious infection of the orbit tissues and commonly affects children. It is very important to know the symptoms and treat them properly.
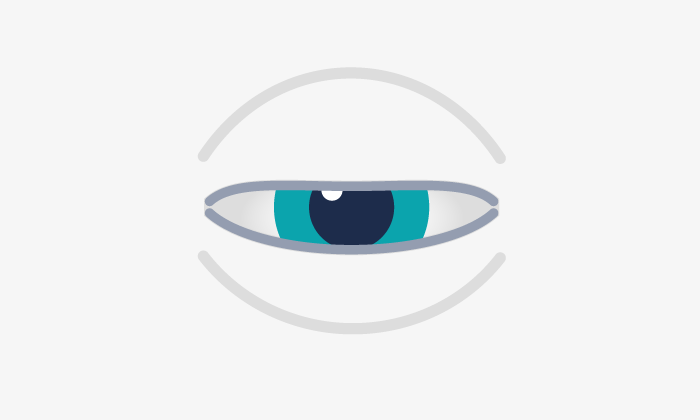

Palpebral ptosis is the dropping of the upper eyelid and is one of the most common oculoplastic problems. This anomalous position is usually caused by a dysfunction of the lifting muscle.

Both the pediatrict cataract and the one that derives from aging, consist of a clounding of the natural crystalline lens of the eye, which can cause blurred vision and even blindness.
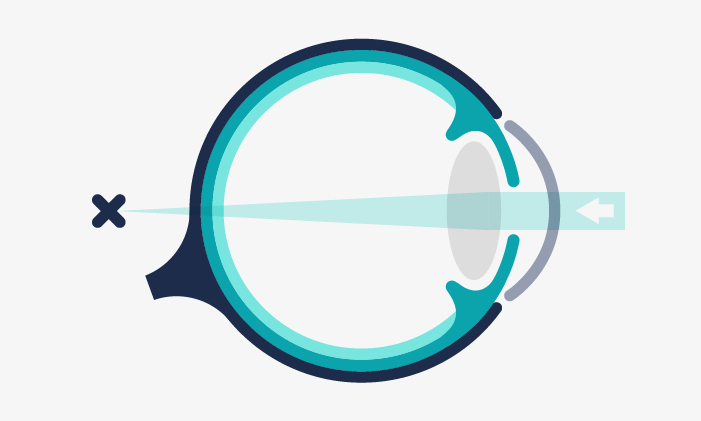
Difficulty to focus in short distances usually begins to appear at 40-45 years old and can be corrected through refractive surgery.
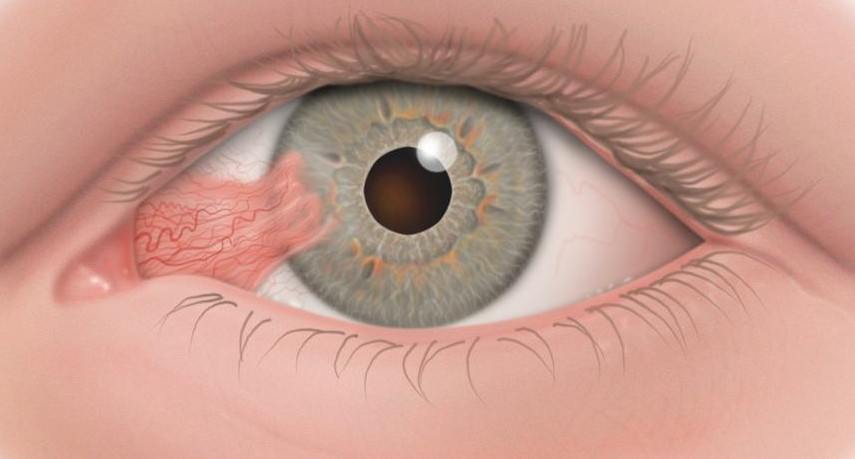
A pterygium is a red and white abnormal growth of the conjunctiva that invades the cornea, most frequently on the side which is closer to the nose, although it can also appear on the external side of the eye, and in both eyes.

Refractive surgery aims to correct refractive errors, such as myopia, hyperopia, astigmatism or presbyopia to obtain a good visual quality and to avoid depending on the use of glasses or contact lenses.
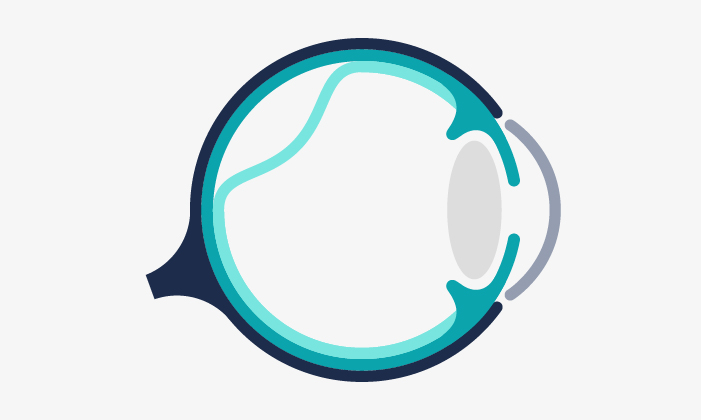

In most cases, the vision can be recovered after a surgery for retinal detachment: But if it is not treated, the patient’s vision could be irrevocably lost.
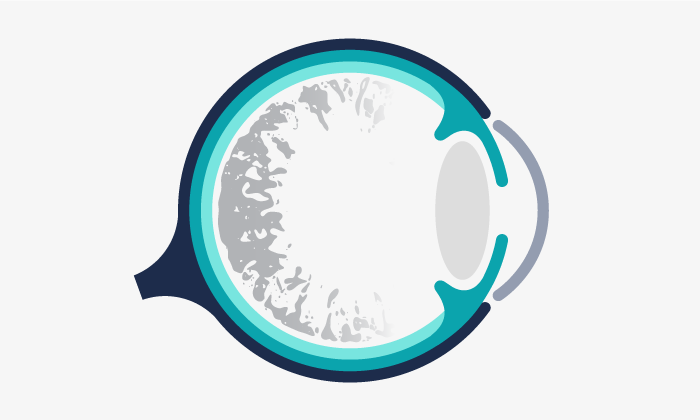

Retinitis pigmentosa is a kind of inhereted retinal disorder that affects the retina and causes a slow vision loss. It begins with a loss of night and lateral vision and eventually causes blindness.
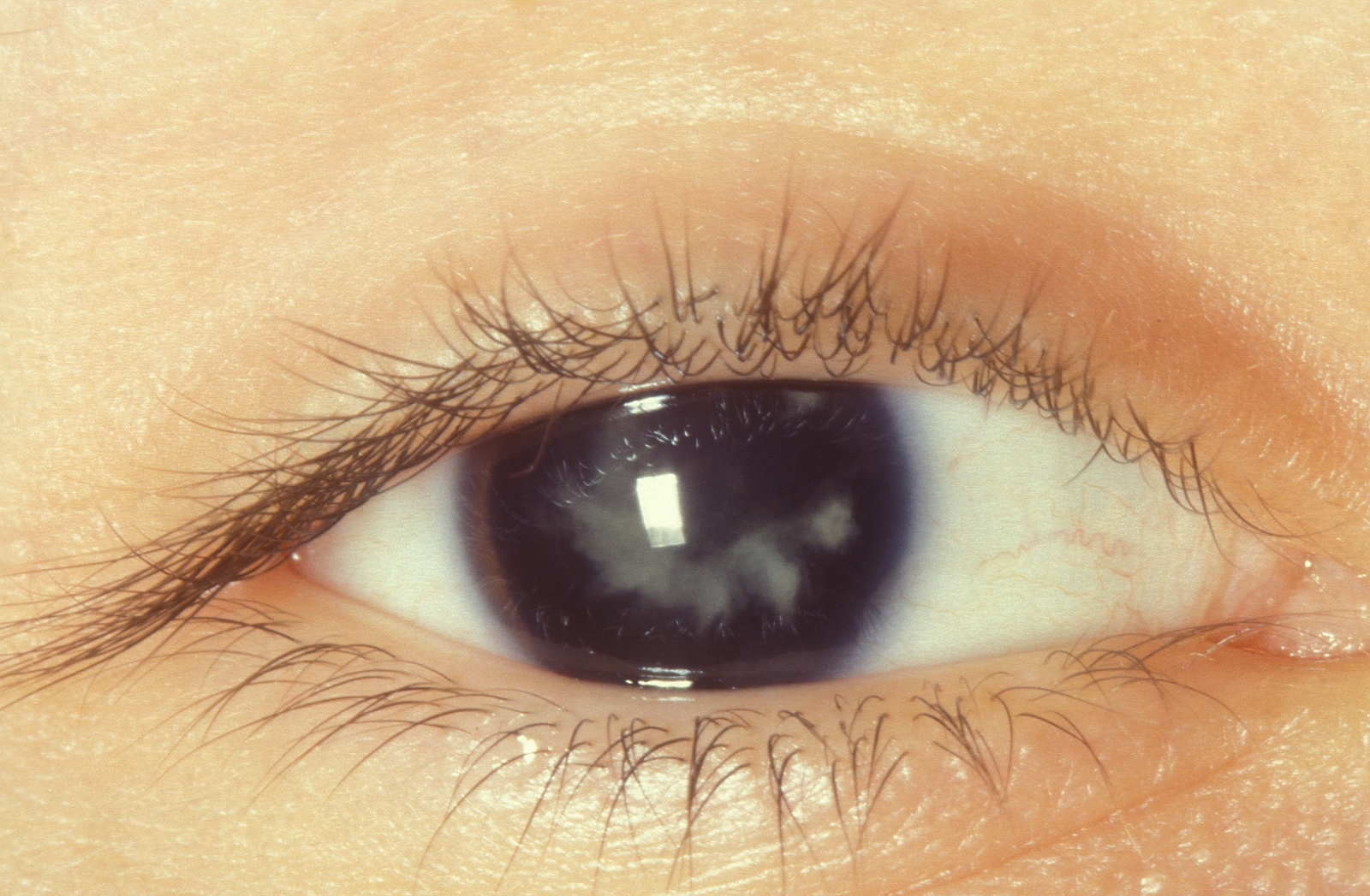
Secondary cataract or after-cataract is an opacification of the posterior capsule of the lens that may appear after having undergone a cataract extraction.
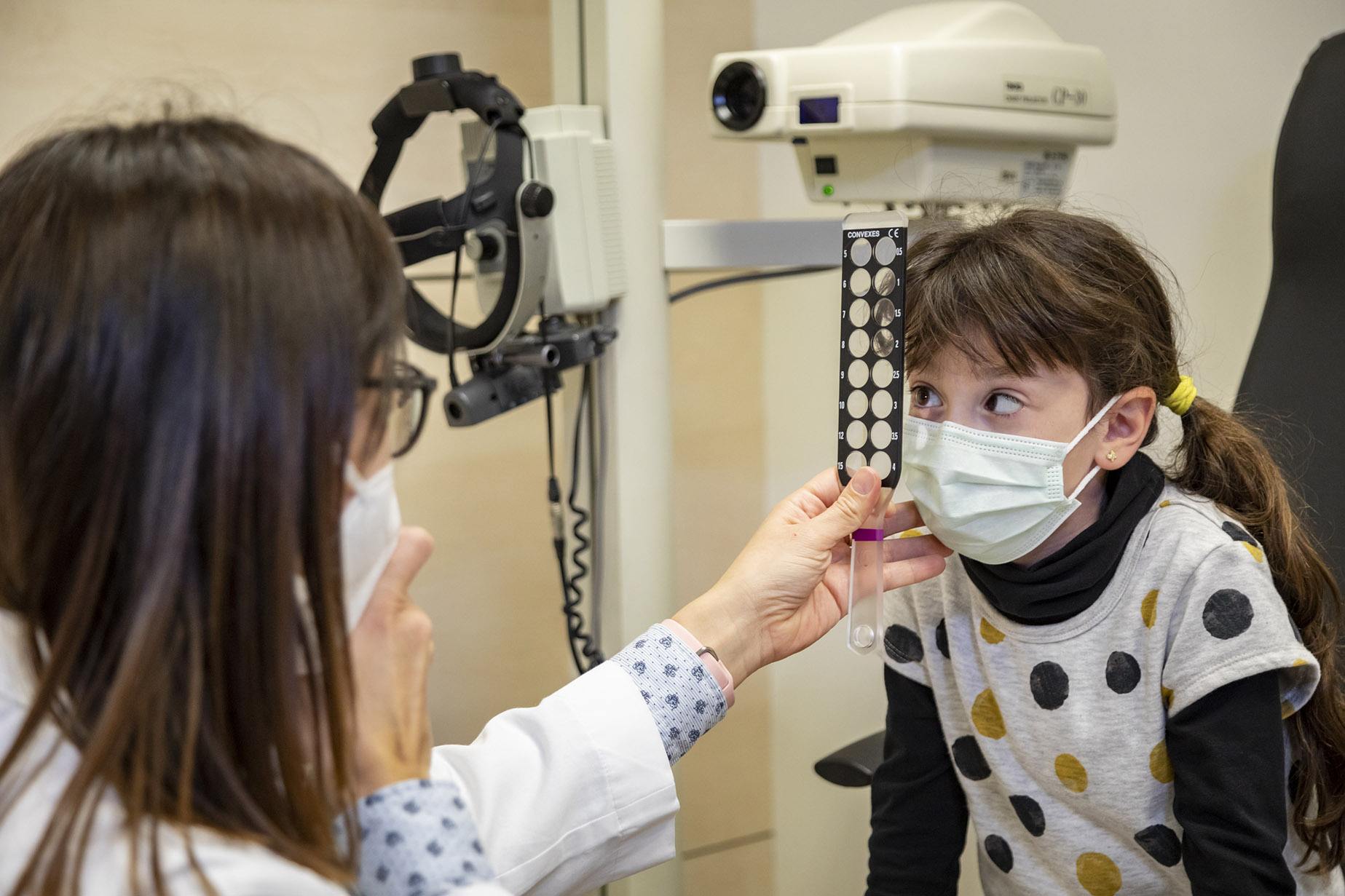
We speak of childhood strabismus when a child suffers an alteration in the alignment of the eyes that causes them not to look simultaneously at the same point. Strabismus can occur in adults too.

A stye is a small, painful lump on the eyelid that may contain pus. It is usually caused by an infection of the Meibomian or Zeiss glands and It can be found both on the inside and outside of the eyelid.
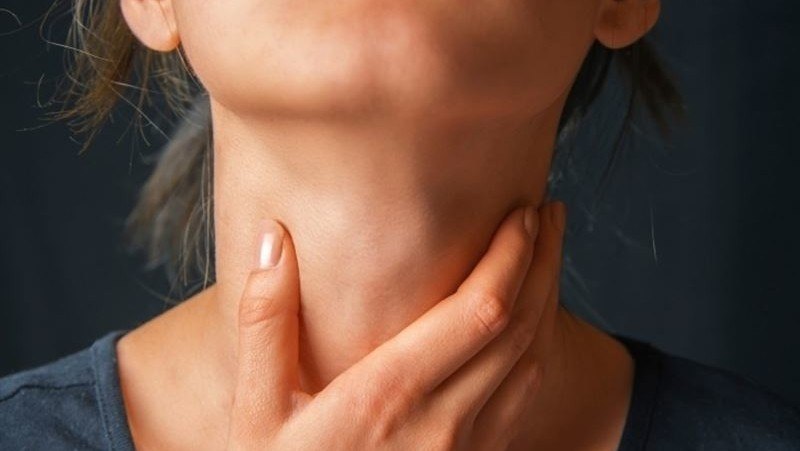
Thyroid orbitopathy is an affectation of the periocular tissues that is associated with autoimmune diseases of the thyroid gland, such as hyperthyroidism. This disease affects mostly adult women and is associated with smoking.

The term uveitis refers to a range of inflammatory conditions that affect the middle layer of the eye known as uvea. Different types of uveitis have different symptoms, causes and treatments.

A vitreous detachment is the separation of the vitreous humour from its attachment points on the retina. This causes a sudden appearance of spots in the form of spider webs or flashing lights.

A vitreous hemorrhage is the presence of blood within the eye cavity that is filled with vitreous humor, a clear substance that fills up to two thirds of the eyeball total volume.
Contact us or request an appointment with our medical team.